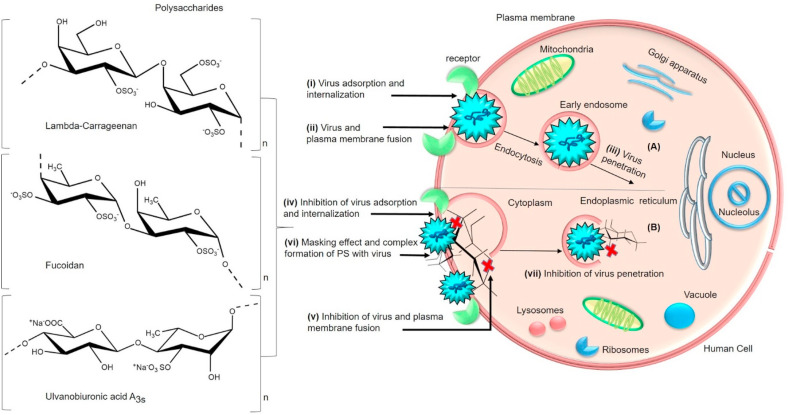
Fig. 5.
(A) General schematic representation of the virus lifecycle post attachment into the host cell- (i) Virus adsorption and internalization after the attachment to the receptor (ii) initiation of fusion event by the virus with plasma membrane of the host cell via endocytosis and its transportation/translocation to the cytoplasm leading to (iii) virus penetration [225,226]. (B) Mode of antiviral action of sulfated polysaccharides (Lambda-carrageenan, Fucoidan, Ulvanobiuronicacid A3s) (iv) inhibition of virus adsorption and internalization (v) inhibition of membrane fusion (plasma membrane) and (vii) inhibition of virus penetration by the interaction of polysaccharides that confers (vi) masking effect, complex formation and destabilizing of fusion peptides (Table 1). (Section 5.2).