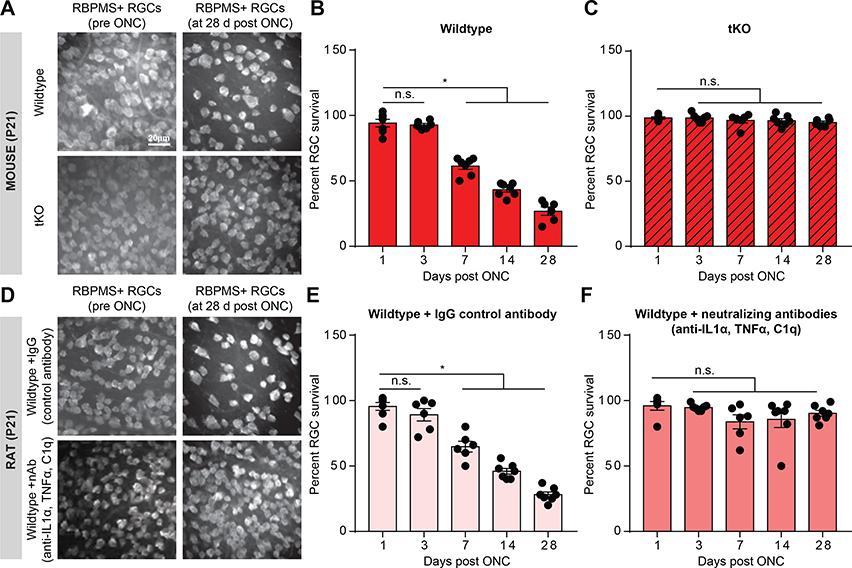
FIGURE 1. Reactive astrocytes drive death of retinal ganglion cells.
A. RBPMS (RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing, an RGC marker) immunostaining of whole-mount mouse retinas showing decreased number of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) following optic nerve crush (ONC) at 28 days, which was prevented in Il1a−/−Tnf−/−C1qa−/− (tKO) mice. B-C. Quantification of RGC survival 1,3, 7,14, and 28 days following optic nerve crush in wild-type (B) and tKO (C) mice. D. RBPMS immunostaining of whole-mount rat retinas showing decreased number of RGCs 28 days following ONC and IgG control antibody injection (E) which was prevented with Il-1α, TNFα, and C1q neutralizing antibody treatment (F). Data normalized to contralateral un-manipulated eye. * P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Individual data points are plotted and represent individual animals, while bars represent mean ± s.e.m. Scale bar is 20 μm for all micrographs in A/D.