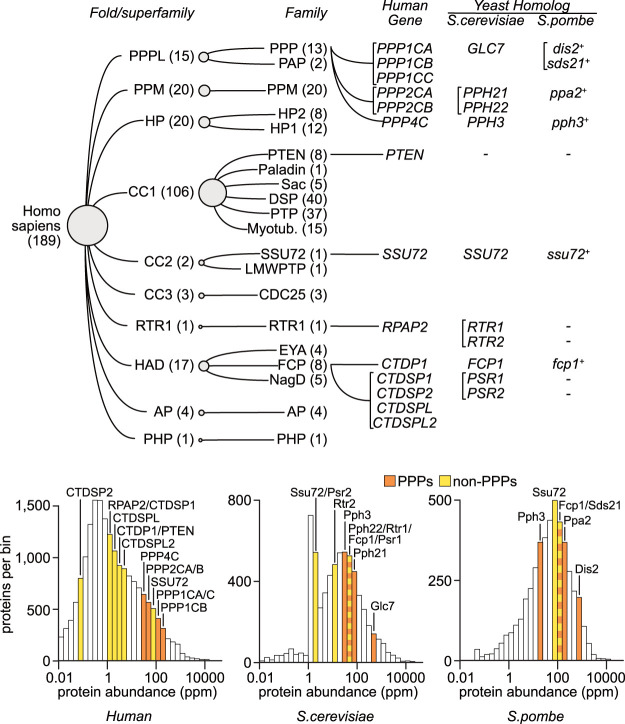
Figure 2.
Human and yeast protein phosphatases implicated in RNAPII transcription. (Top) Hierarchical classification of 189 described human protein phosphatases (Chen et al. 2017). The “human gene” column lists genes encoding phosphatases involved in RNAPII transcription. For these genes, the corresponding homologs in S. cerevisiae or S. pombe are reported. For PPPs, only genes encoding catalytic subunits are included. In parentheses we list the numbers of phosphatases belonging to the respective human family or superfamily. In brackets we group paralogous genes. Layout is adapted from http://phosphatome.net. Homologous genes in different species are reported according to Homologene (http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/homologene) or Chen et al. (2017). (Bottom) Phosphoprotein phosphatases (PPPs) are typically more abundant than non-PPPs in human and yeast proteomes. Proteins are grouped in bins based on their abundance in the proteome. Bins containing transcription-related phosphatases (see top panel) are colored based on whether they are PPPs or not. Proteomic data were obtained and histogram layout was adapted from http://pax-db.org. (ppm) Parts per million.