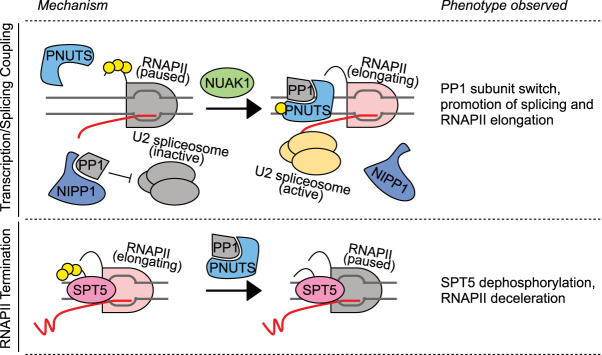
Figure 5.
The PP1-PNUTS holoenzyme acts at multiple steps of transcription. (Top) PP1-PNUTS activity couples transcription to splicing. PNUTS is recruited to RNAPII paused at the first exon–intron boundary but lacks the PP1 catalytic subunit. Concomitantly, PP1 joins another holoenzyme (likely with the NIPP1 splicing factor) and inhibits the U2 spliceosome. The NUAK1 kinase phosphorylates PNUTS and triggers a PP1 subunit switch to bind PNUTS, thereby promoting both pause release and splicing activation (Cossa et al. 2020). (Bottom) PP1-PNUTS is required for efficient termination. PP1-PNUTS dephosphorylates SPT5, slowing RNAPII elongation and ensuring proper, spatially precise termination (Kecman et al. 2018; Parua et al. 2018; Cortazar et al. 2019; Cossa et al. 2020; Eaton et al. 2020; Parua et al. 2020). (Yellow circles) Phosphorylation.