Figure 6.
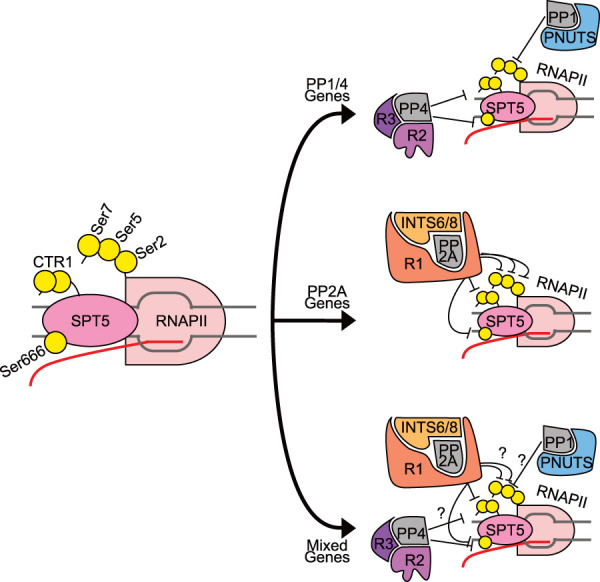
Different PPP holoenzymes cooperate during RNAPII pausing. (Left) Relevant phosphorylation sites on SPT5 and RNAPII. SPT5 C-terminal repeat region 1 (CTR1) typically contains Thr-Pro repeats, where Thr can be phosphorylated by CDK9 (e.g., Thr806 in human SPT5). SPT5 contains another region—the KOW4–KOW5 linker—with multiple Ser residues phosphorylated by CDK9 (including Ser666 in human SPT5). The RNAPII CTD contains multiple heptad repeats, which include phosphorylated residues Ser2, Ser5, and Ser7 (Tyr1 and Thr4 are omitted for clarity). Different PPP family phosphatases have been proposed to act at the promoter-proximal pause, as indicated at right. We speculate that these enzymes might act at different, hypothetical gene classes: “PP1/PP4 genes,” at which PP4 targets SPT5 (Parua et al. 2020) and PP1-PNUTS dephosphorylates pSer5 (Wu et al. 2018; Landsverk et al. 2020); “PP2A genes,” at which PP2A-PPP2R1A, associated with the Integrator, targets both SPT5 and RNAPII residues (Huang et al. 2020; Zheng et al. 2020; Vervoort et al. 2021), and “mixed genes,” where RNAPII and SPT5 are targeted by PP1, PP2A, and PP4 holoenzymes.
