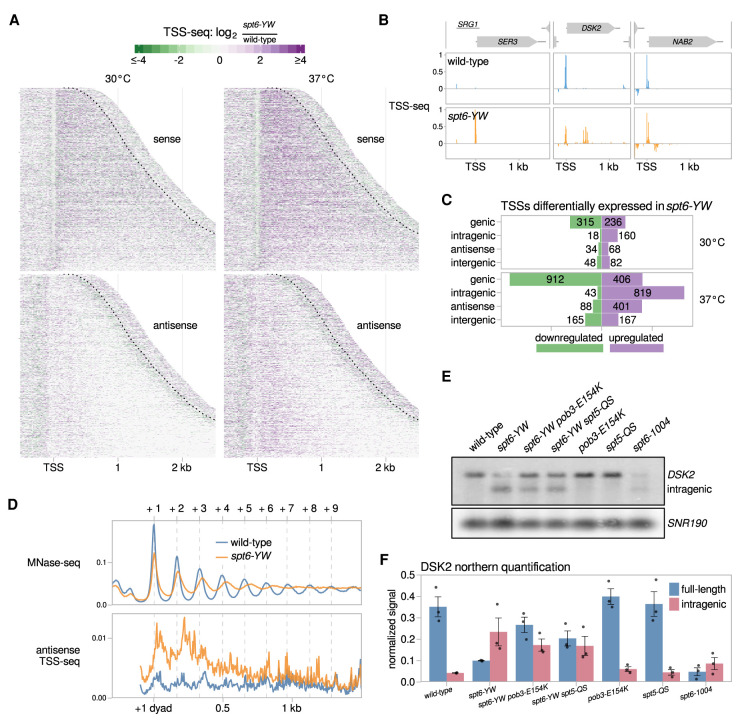
Figure 3.
The spt6-YW mutation causes altered sense and antisense transcription. (A) Heat maps of the ratio of TSS-seq signal in the spt6-YW (FY3223) strain over wild type (FY87), grown at 30°C or with an 80 min shift to 37°C. Data are shown for the sense and antisense strands of 3087 nonoverlapping verified coding genes aligned by wild-type genic TSS and sorted by length. The region shown for each gene extends up to 300 nt 3′ from the cleavage and polyadenylation site (CPS), which is indicated by the dotted line. (B) Examples of altered mRNA level (SER3), intragenic initiation (DSK2), and antisense initiation (NAB2) in spt6-YW. Relative TSS-seq signal in wild-type and spt6-YW strains shifted to 37°C is shown for each region, with sense and antisense signals plotted above and below the X-axis, respectively. The signal is independently scaled for each region shown. (C) Bar plots showing the number of TSS-seq peaks differentially expressed in spt6-YW versus wild type. “Intragenic” and “antisense” refer to sense strand and antisense strand intragenic TSSs, respectively. (D, top panel) The average positions of the +1 through +9 nucleosome dyads in wild type and spt6-YW as determined from MNase-seq are indicated with vertical dashed lines. (Bottom panel) The median antisense TSS-seq signal in wild type and spt6-YW at 37°C, over 3086 nonoverlapping verified coding genes aligned by wild type +1 nucleosome dyad. (E) Northern analysis of the DSK2 gene after a shift to 37°C, using a probe from the 3′ region of DSK2, to assay DSK2 full-length and intragenic transcripts. SNR190 served as the loading control. (F) Quantification of the full-length and intragenic DSK2 transcript levels from three Northerns. Error bars indicate the mean ± standard error of the Northern signal for DSK2 normalized to the SNR190 signal.