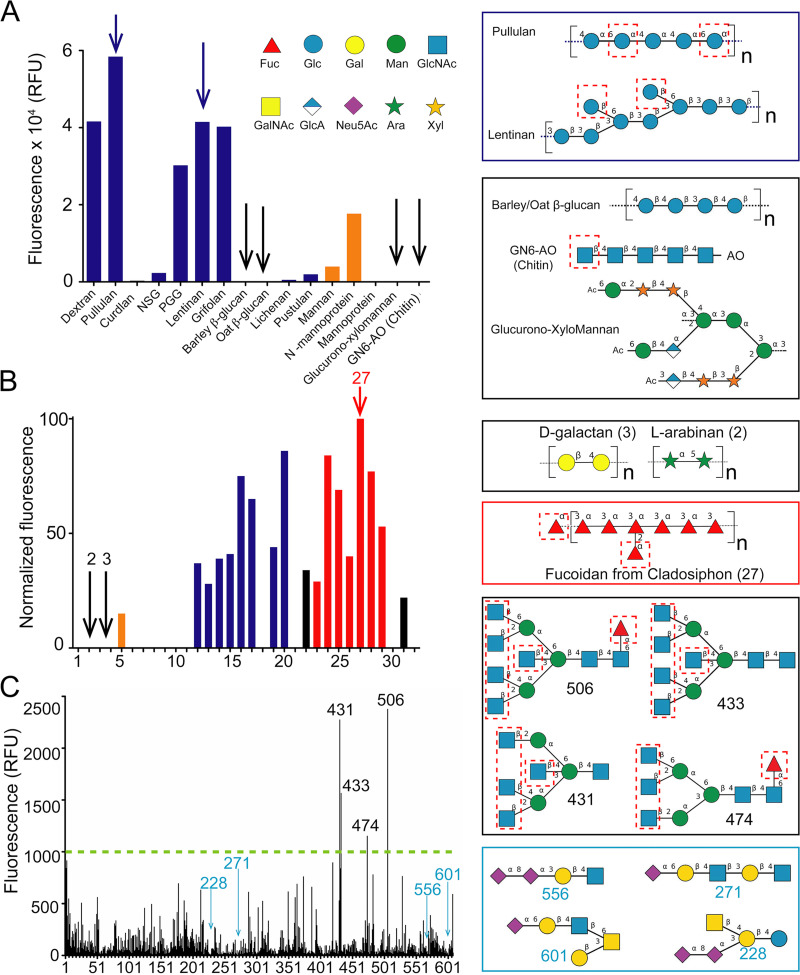
FIG 4.
Binding of MpPA14 to sugar oligomers identified by three different glycan microarrays. (A) Microbial glycan array analysis conducted at the Imperial College Glycosciences Laboratory. Data bars showing binding intensity for glucans and mannans are colored blue and orange, respectively. Examples of strong binders are drawn in the blue box (top right, blue arrows in the graph), while those for weak binders are drawn below (black arrows in the graph). The putative sites for MpPA14 binding to the glycans are indicated by dashed red boxes. Glycan nomenclature symbols are included. Abbreviations are as follows: Fuc, l-fucose; Glc, glucose; Gal, galactose; Man, mannose; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; GalNAc, N-acetyl-galactosamine; GlcA, glucuronic acid; Neu5Ac, N-acetyl-neuraminic acid; Ara, l-arabinose; Xyl, xylose. (B) Microarray data of glycans from marine algae and land plants. Glucans (blue), mannans (orange) fucoidans (red), and other types of glycans (black). Examples of nonbinders (right, black arrows in the graph), while the structure for Cladosiphon fucoidan is shown below (red arrow in the graph). (C) Mammalian glycan array analyzed at the Consortium for Functional Glycomics. Representative structures for the strong MpPA14 binders (black box) and nonbinders (blue box) are drawn on the right.