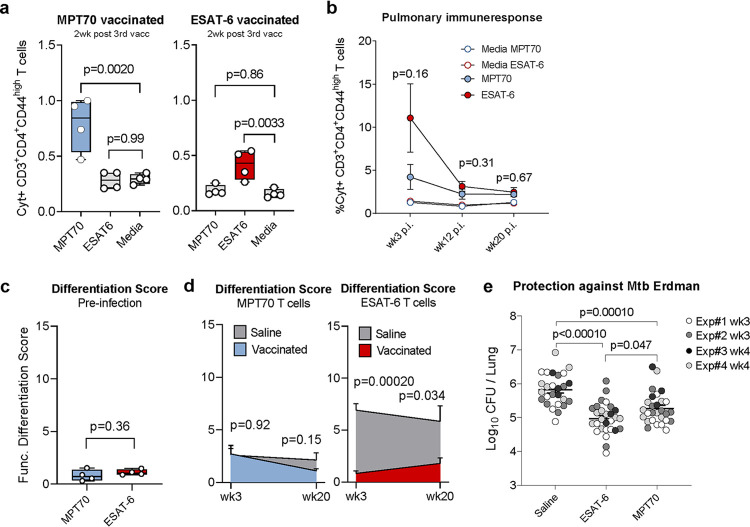
FIG 3.
The impact of MPT70 immunization on alleviating infection-driven T cell differentiation is lower than immunization with ESAT-6. Female CB6F1 mice were immunized with either MPT70 or ESAT-6 recombinant protein three times s.c. and challenged with Mtb Erdman 6 weeks after the third immunization. (a) Frequency of MPT70- and ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cells in the spleen 2 weeks after the third vaccination (n = 4). Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test was used to assess statistical differences. (b) Frequency of MPT70- and ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cells in the lung at weeks 3, 12, and 20 after Mtb infection (n = 4). Values shown are means ± SEM. An unpaired t test was used to compare the values for ESAT-6- and MPT70-vaccinated mice. (c) Functional differentiation score (FDS) of MPT70 and ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cells preinfection in the spleen (n = 4). An unpaired t test was used to assess statistical differences. (d) FDS of MPT70- and ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cells 3 and 20 weeks after Mtb infection in the lungs of vaccinated mice and mice injected with saline (n = 4). Values shown are means ± SEM. An unpaired t test was used to compare individual time points. Flow cytometry gating is shown as depicted in Fig. S1a, using the antibodies shown in Table 4. (e) The bacterial burden was determined in the lungs of mice injected with saline or mice vaccinated with MPT70 and ESAT-6 3 to 4 weeks after Mtb infection (n = 26 to 28). The graph shows the results of four individual experiments (experiment 4 has already been published in reference 29). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was used to assess statistical differences.