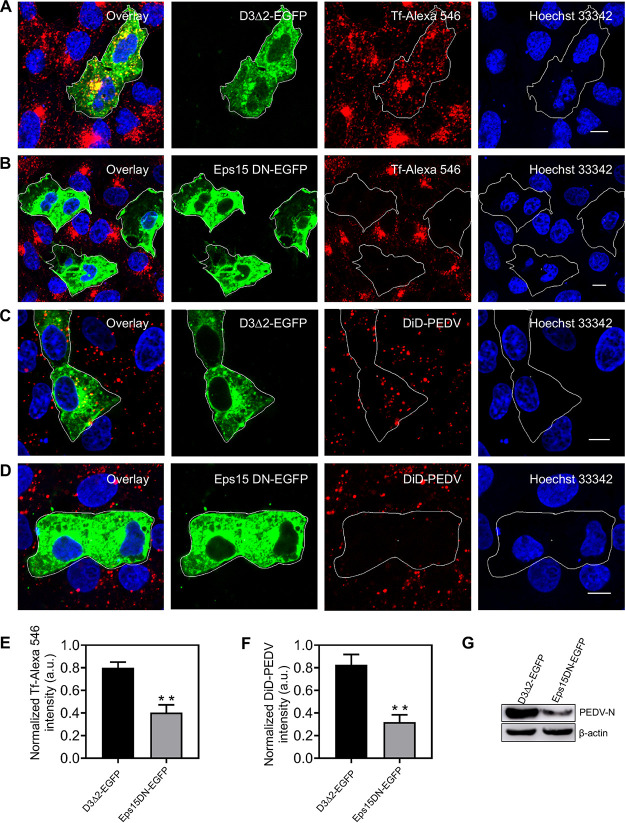
FIG 3.
Disruption of CME by overexpressing Eps15 DN hampers PEDV entry. (A, B) Fluorescence images of the uptake of transferrin in cells expressing D3Δ2-EGFP and Eps15 DN-EGFP. As a verification of Eps15 DN inhibition efficiency, Vero CCL81 cells were transfected with plasmid D3Δ2-EGFP or Eps15 DN-EGFP; after 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated with Tf-Alexa 546 at 37°C for 30 min and then fixed and imaged. (C, D) Fluorescence images of the uptake of DiD-labeled PEDV in cells expressing D3Δ2-EGFP or Eps15 DN-EGFP. Vero CCL81 cells were transfected with plasmid D3Δ2-EGFP or Eps15 DN-EGFP; after 24 h of transfection, cells were infected with DiD-labeled PEDVs (MOI, 10) at 37°C for 30 min and then fixed and imaged. (E, F) To quantify the internalization dependency of Tf and PEDVs on the expression of each plasmid, in cells transfected with plasmid D3Δ2-EGFP or Eps15 DN-EGFP, fluorescence intensities of Tf-Alexa 546 and DiD-labeled PEDV were measured and normalized according to those of untransfected cells. Error bars denote mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (G) Cells were transfected with plasmid D3Δ2-EGFP or Eps15 DN-EGFP. After a 24-h transfection, cells were infected with PEDVs (MOI, 1) and cultured at 37°C for 6 h. Then, samples were collected and analyzed by Western blotting with corresponding antibodies. PEDV-infected cells transfecting the D3Δ2-EGFP plasmid served as controls. **, P < 0.01. Scale bar, 10 μm.