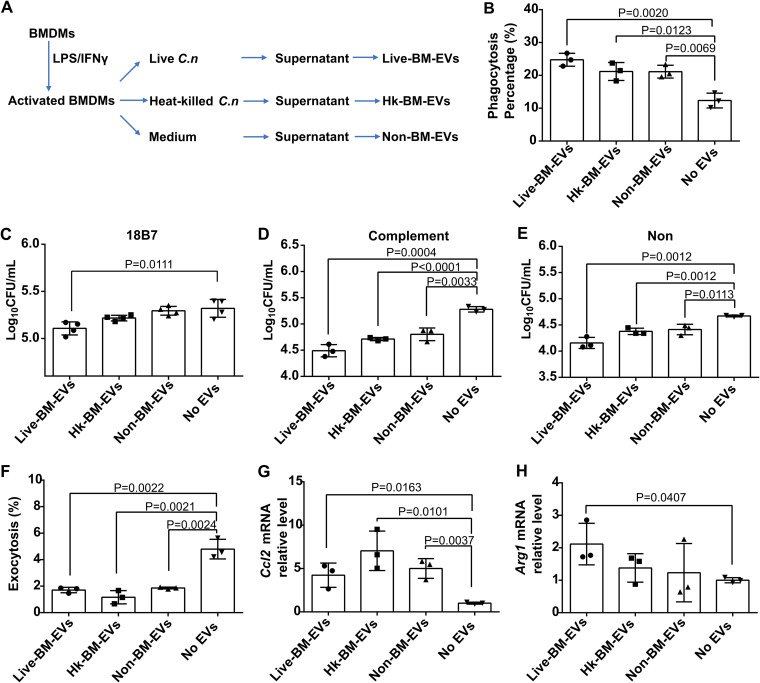
FIG 2.
All three types of activated BMDM-EVs triggered increased antifungal activity of naive BMDMs during C. neoformans (C.n) infection, while live-BM-EVs (EVs from live C. neoformans-infected activated BMDMs) had the highest potential. (A) Flowchart of harvesting of the three types of EV samples. (B) Phagocytosis percentages of naive BMDMs after incubation with three types of EV samples. At least 100 macrophages were counted for each group. (C to E) Fungicidal activity of naive BMDMs after incubation with three types of EV samples with opsonin 18B7 (C), complement (D), or none (E). (F) Nonlytic exocytosis of naive BMDMs after incubation with three types of EV samples. (G and H) Macrophage polarization, as measured by mRNA levels of Ccl2 (G) and Arg1 (H), in naive BMDMs after incubation with three types of EV samples. Non-BM-EVs, EVs from activated BMDMs without C. neoformans infection; No EVs, EV-nontreated macrophages; Hk, heat killed. Data are shown as the means ± SD from at least three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. An unpaired t test was used to calculate P values.