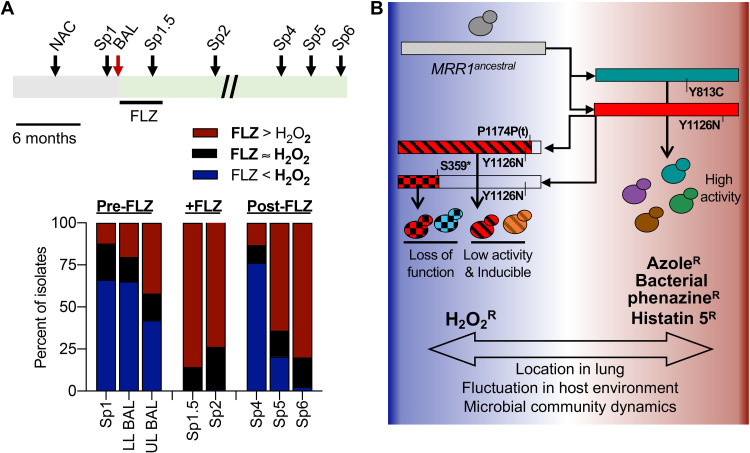
FIG 5.
Trade-off between FLZ and H2O2 resistance persists in evolving C. lusitaniae populations during a chronic lung infection. (A) Schematic of sampling timeline (top) and histogram of the number of isolates that (i) were mostly uninhibited on FLZ, but were inhibited by H2O2 (red), (ii) were mostly uninhibited on H2O2 but were inhibited by FLZ (blue), or (iii) were uninhibited under both conditions (black). For the schematic, the gray bar represents the 6 to 10 months before the BAL during which this patient was identified as being colonized by non-albicans Candida (NAC) species. C. lusitaniae was determined to be the dominate microbe in the upper and lower lobe (UL and LL, respectively) BAL samples (red arrow), which marks the start of the green bar. Sp1 was obtained 1 month before the BAL and was retrospectively also found to contain abundant C. lusitaniae. Sp1.5, Sp2, Sp4, Sp5, and Sp6 were obtained 3, 9, 32, 35, and 38 months, respectively, after the BAL and all contained C. lusitaniae. A 4-month course of FLZ therapy was given after the BAL. Scale bar indicates 6 months. Multiple isolates were collected from each sample/timepoint (n = 38 to 80) and assayed for growth on YPD supplemented with 8 μg/ml FLZ or 4 mM H2O2. Growth was scored as completely inhibited, partially inhibited or uninhibited compared to that of a YPD-only control. (B) Model for the evolution of C. lusitaniae MRR1 in this population. Whole-genome sequencing and mutation analyses suggest that following the initial infection with C. lusitaniae harboring the Mrr1-ancestral variant, a combination of exposure to different stimuli that changed overtime or by locations within the CF lung environment led to the selection for a heterogeneous population. Multiple constitutively active Mrr1 variants arose, and while some persisted over time, others were subsequently mutated again. The secondary mutations causing premature stop codons (represented by shortened bars) resulted in reversion to low Mrr1 activity that was inducible or complete loss of Mrr1 activity. The balance between selective pressures resulted in a heterogeneous population of isolates with varied resistance (R) to biologically and clinically important compounds.