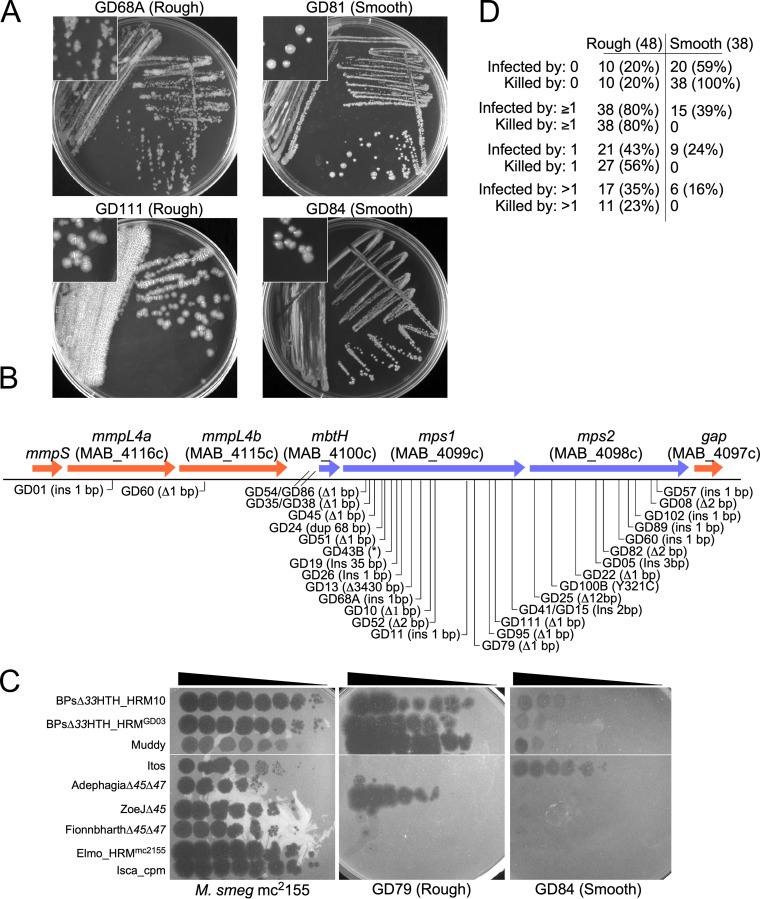
FIG 2.
Smooth and rough M. abscessus morphotypes. (A) Examples of strain colony morphotypes showing strains GD68A and GD111 (both rough) and GD81 and GD84 (both smooth) growing on solid medium. Insets show magnified view of colonies. (B) Mutations contributing to rough colony morphotypes. Rough strain sequences were compared with ATCC 19977 genes involved in GPL synthesis (as shown) and those with small (1 to 2 bp) insertions or deletions are indicated. One mutation (GD100B) is a single base substitution in mps2 and is the sole difference from its smoother counterpart, GD100A. A large spectrum of mutations is observed, although three pairs of rough strains (e.g., GD35 and GD38) have the same mutations. See Table S2 for details. (C) Plaque assay showing infection of M. smegmatis mc2155, M. abscessus GD79 (rough), and M. abscessus GD84 (smooth), as indicated. Ten-fold serial dilutions of phages were spotted from left to right on lawns of each strain, as indicated. (D) Phage susceptibilities of rough and smooth morphotype strains. The numbers of each strain morphotype that are not infected or killed by any phage tested (0), by at least one phage (≥1), by only a single phage (1), or by 2 or more phages (>1), as indicated, are shown. See Fig. 3 legend for details. The total number of strains (86) includes four strain pairs (e.g., A, B) each from a single patient source.