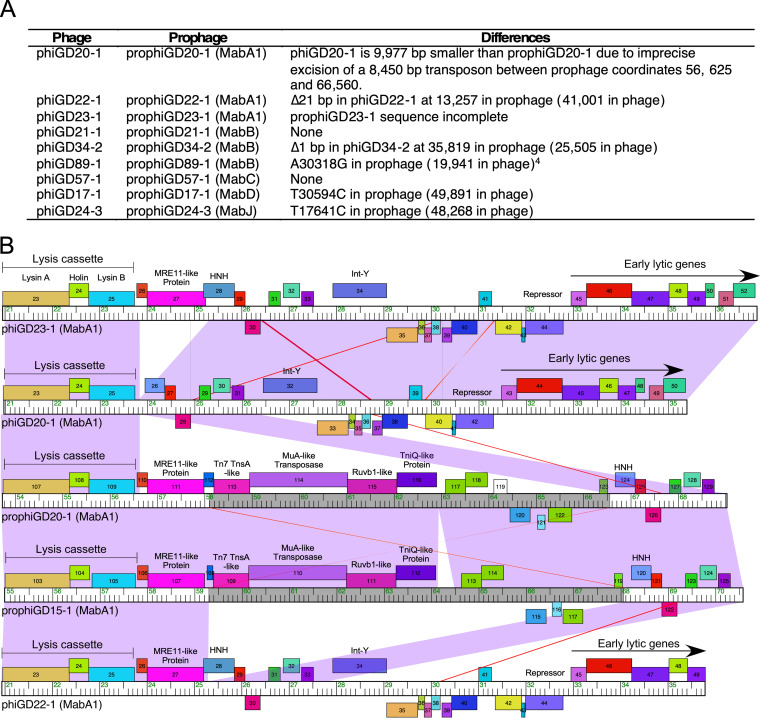
FIG 6.
Comparison of induced phages and their cognate prophages. (A) Comparisons of phage (i.e., phiGDxx) and their cognate prophages (i.e., prophiGDxx) showing genomic differences; phages and prophages are named after the strain they were isolated from. The prophiGD23-1 sequence is incomplete in the WGS assembly and thus cannot be fully compared with phiGD23-1. In phiGD89-1, there are several differences in a region that is well conserved in other MabB phages, including phiGD21-1. Specifically, the sequence 5′-TGGACTACGGCTGAGCAGCA-TGCT (coordinates 30,519 to 30,542) replaces 5′-TGGGCTACGGCTGAGCAGTAGAACT. This is in the location of a predicted rightward early promoter and operator site, and likely inactivates lysogeny. (B) Comparison of phage and prophage genome segments, illustrating the transposon insertions (gray areas on genome rulers) in prophages prophiGD20-1 and prophiGD15-1. Genome annotations and comparisons are illustrated as in Fig. 5D. The alignment illustrates the transposon insertion (comparing phiGD22-1 and prophiGD15-1), and excision of the transposon and flanking gene in phiGD20-1. The transposons in prophiGD20-1 and prophiGD15-1 are closely related but inserted at targets 25 bp apart.