Figure 1. Cryo-EM structure of the C144-S complex illustrates a distinct VH3-53 hNAb binding mode.
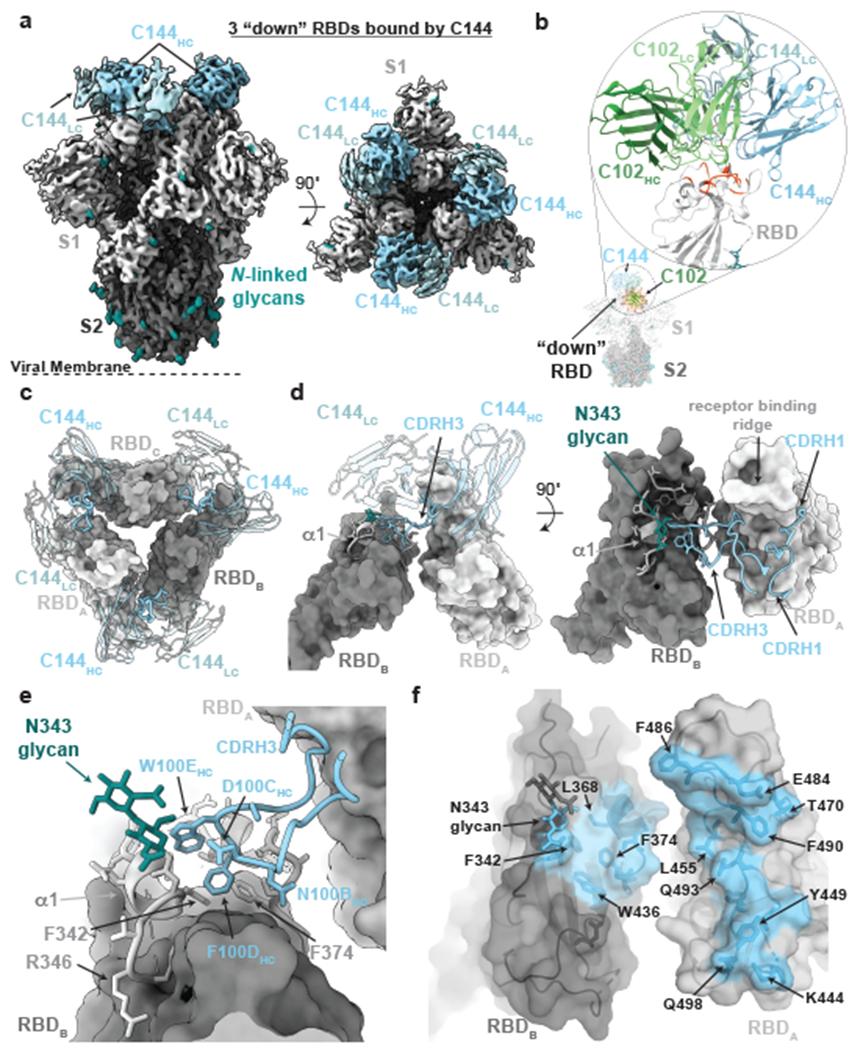
a, 3.2Å cryo-EM density for C144-S trimer complex revealing C144 binding to a closed (3 RBDs “down”) spike conformation. b, Overlay of C102 Fab (from C102-RBD crystal structure; Extended Data Fig.1) and C144 Fab (from C144-S structure) aligned on a RBD monomer. RBD residues corresponding to the ACE2 epitope (orange-red cartoon) are shown on the same RBD for reference. C144 adopts a distinct conformation relative to the C102-like VH3-53/short CDRH3 NAb class, allowing binding to the “down” RBD conformation on trimeric spike, whereas C102-like NAbs can only bind “up” RBDs. c, Quaternary epitope of C144 involving bridging between adjacent RBDs via the CDRH3 loop (illustrated as thicker ribbon). d,e, Close-up view of CDRH3-mediated contacts on adjacent protomer RBD (dark gray). C144 CDRH3 residues F100D and W100E are buried in a hydrophobic pocket comprising the RBD α1 helix, residue F374RBD and the N343RBD-glycan. f, Surface representation of C144 epitope (light blue) across two adjacent RBDs. RBD epitope residues (defined as residues containing atom(s) within 4Å of a Fab atom) are labeled in black.
