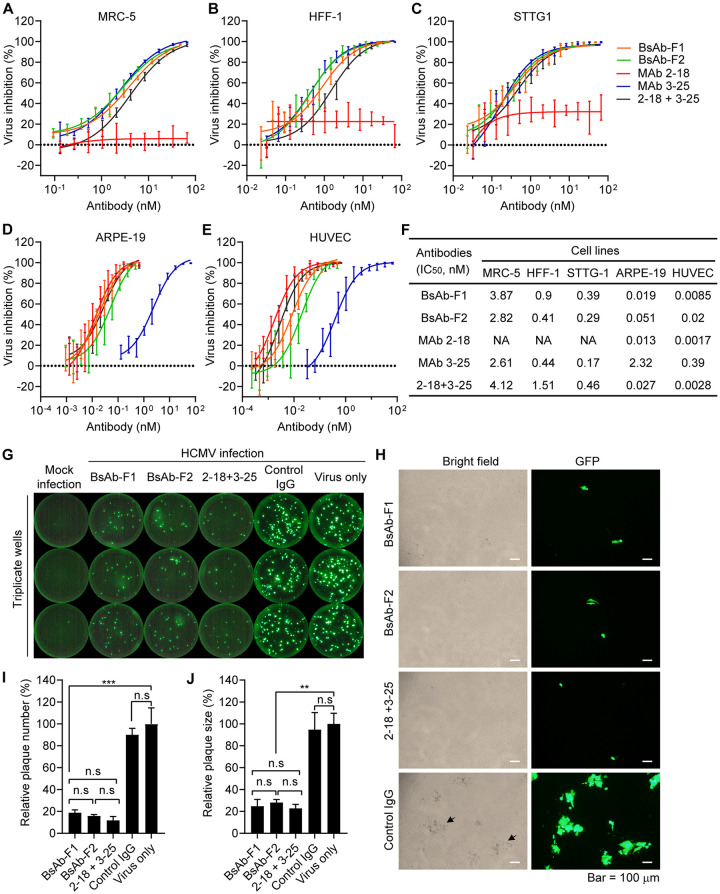
FIG 4.
Functional characterization of HCMV-bispecfic IgG-scFv antibodies in vitro. (A to F) The neutralization efficacies of indicated antibodies against HCMV strain AD169rev-GFP in (A) MRC-5 cells, (B) HFF-1 cells, (C) STTG1 cells, (D) ARPE-19 cells, and (E) HUVECs. (F) The IC50s were calculated by nonlinear fit of virus inhibition percentage versus concentration (nM) using GraphPad Prism 5 software. Data are representative of two independent experiments with four replicate wells for each concentration. (G and H) Inhibition of postinfection viral spreading. Confluent ARPE-19 cells grown in a 96-well plate were infected with AD169rev-GFP. At 3 days postinfection, the virus-containing culture medium was replaced with fresh medium containing 10 μg/ml of the indicated antibodies, and the cells were further cultured. Mock-infected and virus-only wells served as controls. Whole-well GFP images were captured using a CTL Immunospot analyzer at 14 days postinfection. (G) Representative whole-well images for GFP expression. (H) Representative pictures showing the GFP plaques and the cytopathic effects caused by HCMV infection of the same area. Pictures were acquired by an Olympus fluorescence microscope at 14 days postinfection. Size bars = 100 μm. The black arrows indicate examples of cytopathic effects. (I) The number of GFP plaques and (J) the sizes of the GFP plaques in single wells as shown in panel G were quantified by ImageJ software. Data are shown as relative percentages of the number or size of GFP plaques in antibody-treated wells to those of virus-only controls. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. n.s., not significant (P > 0.05); **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. The error bars indicate mean ± SD values from replicate wells.