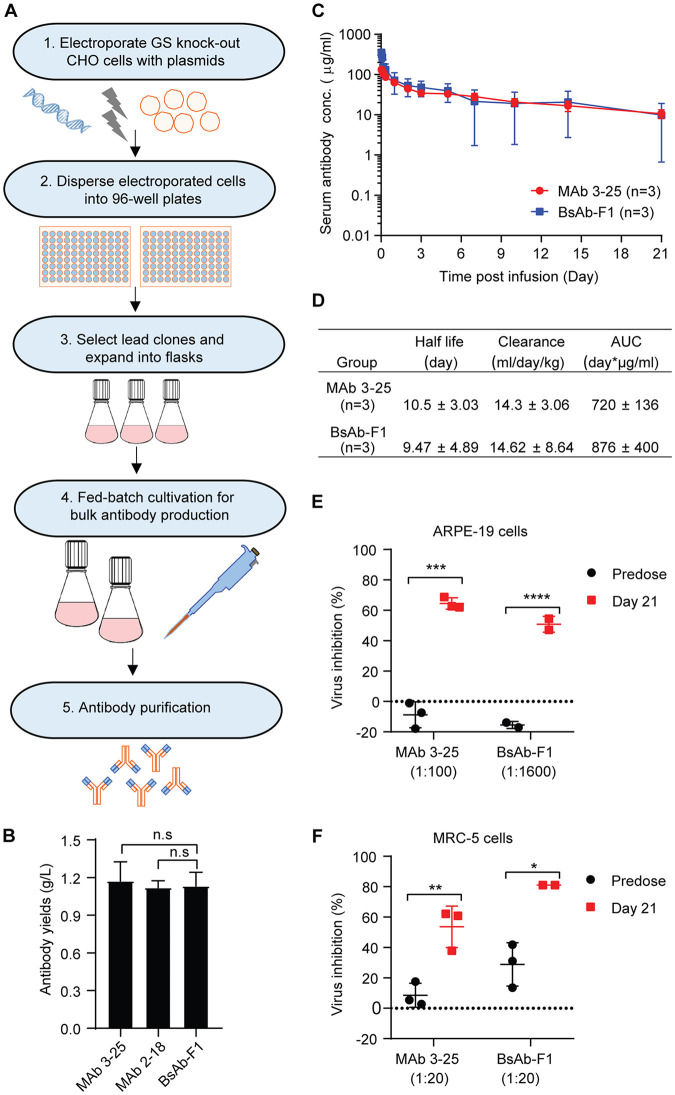
FIG 5.
Single-dose pharmacokinetics study of BsAb-F1 and MAb 3-25 in rhesus macaques. (A) A flowchart for construction of stable CHO cell lines. Linearized plasmids with genes for expression of the heavy chain and light chain of the antibody and glutamine synthetase (GS) were transfected into GS knockout CHO cells by electroporation. The transfected cells were dispersed into 96-well plates and cultured under selection medium without glutamine. After 3 weeks, the level of antibody secreted in the culture medium from wells of expanded clones was quantified by ELISA. The high-yield clones were selected for expansion in flasks and used for bulk antibody production by a fed-batch method. (B) The yields of MAb 2-18, MAb 3-25, and BsAb-F1 by lead clones at 16 days postinoculation using fed-batch cultivation. (C) Two groups of rhesus macaques (n = 3) were injected intravenously with single dose (10 mg/kg) of MAb 3-25 or BsAb-F1. The serum concentrations of injected antibodies at predose and multiple time points (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h and 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, and 21 days) postinjection were quantified by ELISA. (D) Pharmacokinetics parameters were calculated by noncompartmental analysis using Phoenix 32 WinNonlin (8.1.0.3530) software (Certara). Data from three animals are shown as mean ± SD. (E and F) The predose and 21-day postinjection serum samples at indicated dilutions were used for HCMV neutralization assays in ARPE-19 cells (E) and MRC-5 cells (F). The unpaired two-tailed Student's t test was used to determine statistical significance. n.s., not significant (P > 0.05); *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. The error bars indicate mean ± SD values from three animals in each group.