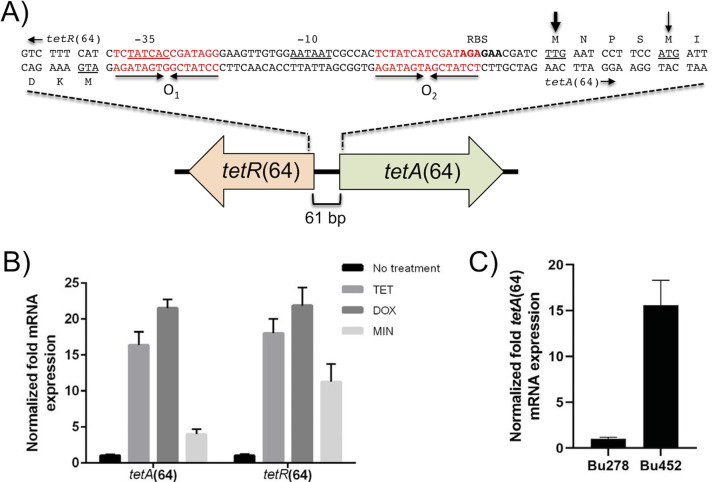
FIG 1.
Genetic organization and functional analysis of B. ubonensis Bu278 tetR(64)-tetA(64) resistance locus. (A) Gene organization and sequence of intergenic region. The tetA(64) gene encoding the TetA(64) MFS efflux pump and the tetR(64) gene encoding the TetR(64) regulatory protein are separated by the 61-bp intergenic region (IR). The thin arrow indicates the TetA(64) ATG start codon (underlined) annotated in the B. ubonensis genome sequences. The more likely TTG start codon (underlined) that is preceded by a putative ribosome-binding site (RBS; bolded) is marked with a thick arrow. The IR contains two regions of imperfect dyad symmetry (inverted arrows), the putative O1 and O2 operator sites, whose sequences are in red type. The predicted −35 and −10 regions of the tetA(64) promoter that share significant homology with bacterial σ70 promoters are underlined. The tetR(64)-tetA(64) region of Bu278 was extracted from GenBank assembly accession no. GCA_002276145.1 and is available via GenBank accession no. MW052058. (B) Transcription of tetA(64) and tetR(64) is induced by tetracyclines. Cells of Bu278 were grown in LB medium in the absence or presence of the indicated tetracyclines, and total RNA was isolated. The tetA(64) and tetR(64) mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR. Expression levels are shown relative to uninduced cells. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of comparisons between three biological replicates, of which each was performed in technical triplicate. (C) Transcription of tetA(64) is constitutive in a ΔtetR(64) mutant. Cells of Bu278 and its ΔtetR(64) derivative Bp452 were grown in LB medium, and total RNA was isolated. The tetA(64) mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR. Expression levels are shown relative to LB-grown uninduced Bu278 cells. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of comparisons between three biological replicates, of which each was performed in technical triplicate.