FIG 3.
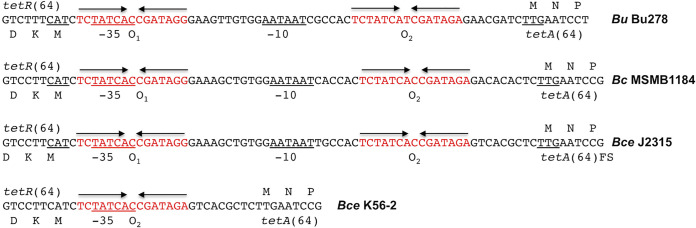
Conservation of the tetR(64)-tetA(64) intergenic region (IR) in Bcc bacteria. Shown are sequences that are representative of wild-type tetR(64)-tetA(64) IRs (B. ubonensis Bu278, B. cepacia MSMB1184WGS, and B. cenocepacia J2315) and a mutant IR (B. cenocepacia K56-2). Features shown include the predicted amino-terminal amino acid sequence of the tetR(64) and tetA(64) genes on the left and right, respectively, the predicted −35 and −10 regions of the tetA(64) promoter, and the putative O1 and O2 operator sites. The B. cepacia MSMB1184WGS and B. cenocepacia J2315 IRs are identical in length (63 nucleotides), compared with 61 nucleotides for Bu278. The B. cenocepacia K56-2 IR is only 25 nucleotides long and only contains an O2 operator site and a putative −35 sequence but no −10 sequence. FS, frame-shifted and truncated TetA(64) in B. cenocepacia J2315.