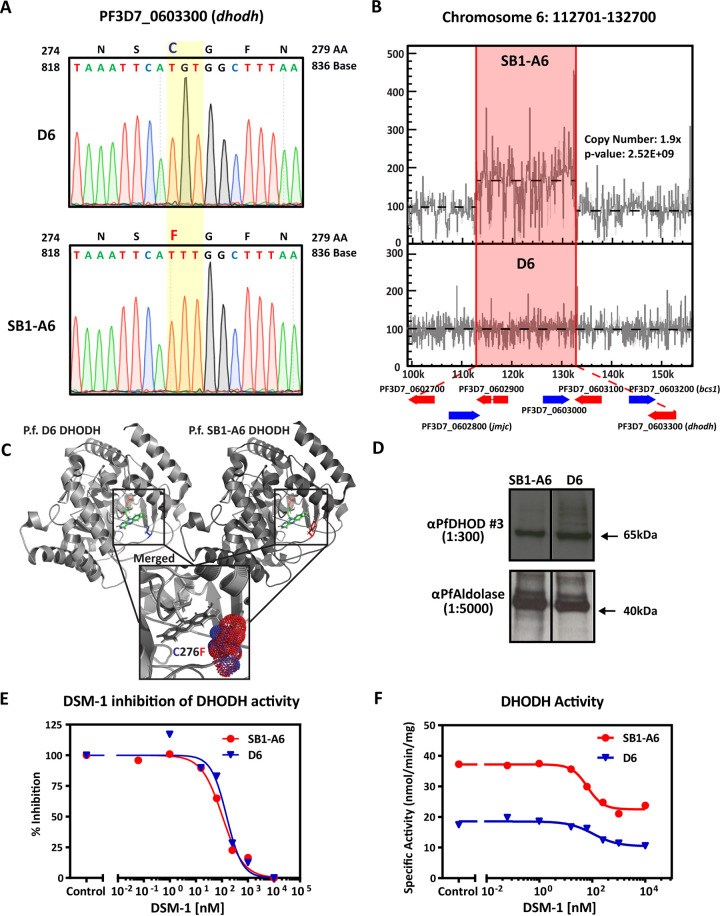
FIG 2.
Genetic and molecular differences in P. falciparum strain SB1-A6. (A) Whole-genome sequencing revealed a point mutation in PF3D7_0603300 (pfdhodh), and this mutation was verified by Sanger sequencing. A trace of the PfDHODH coding sequence is shown from nucleotide 818 to 836 and the single nucleotide polymorphism change from the parental D6 to SB1-A6 at nucleotide G827T (yellow highlight), which results in the amino acid change C276F. Additionally, WGS revealed a 1.9× copy number increase of an ∼20-kb region (red highlight) on chromosome 6, which includes PF3D7_0603300 (pfdhodh) (B). Copy number increase was calculated and graphically represented using Intansv (version 0.99.3). (C) Structural comparisons of wild-type (PDB accession number 4RX0, light gray, C276 highlighted in blue) and mutant (PDB accession number 6E0B, dark gray, C276F highlighted in red) PfDHODH bound with flavin mononucleotide (FMN) as well as the merged structure surrounding amino acid 276 (inset, cysteine in blue and phenylalanine in red, represent the isosurface of each sidechain) were made using PyMOL 2.3.4. (D) Western blot analysis of the PfDHODH expression in both D6 and SB1-A6 probed with mouse anti-PfDHODH antibody (1:300) compared to PfAldolase (mouse anti-PfAldolase-HRP, 1:5,000) as a loading control. Percent inhibition of PfDHODH activity (E) and capture of total PfDHODH activity (F) in isolated mitochondria from SB1-A6 (red) and D6 (blue) in the presence of titrating concentrations of DSM-1.