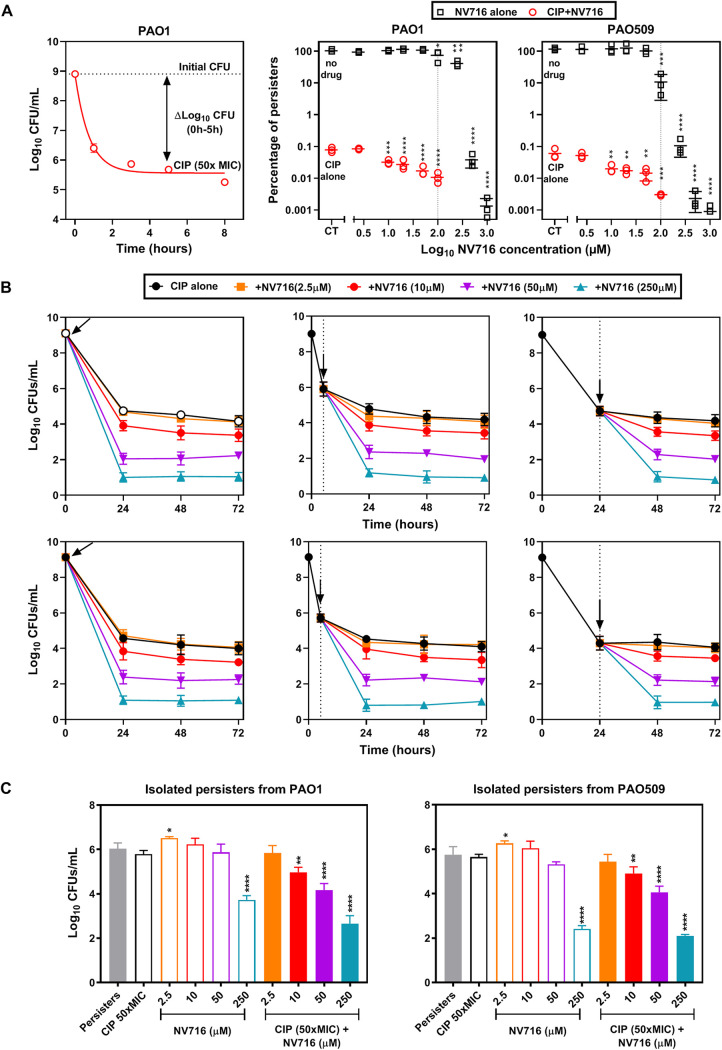
FIG 5.
Influence of NV716 on persisters selected by ciprofloxacin. (A) Persister fraction assay for ciprofloxacin (CIP) alone, NV716 alone, or their combination against reference strains. Left: kill curve of a stationary-phase culture of PAO1 exposed to ciprofloxacin at 50× MIC over time. The persister fraction is calculated as the difference in CFU counts between control and treated samples at 5 h, when a plateau value has been reached. Right: percentage of persister cells (compared to the CFU counts of untreated samples) after 5 h of incubation with increasing concentrations of NV716 alone or combined with 50× MIC of ciprofloxacin. All data are expressed as means ± SEM (triplicates from three experiments). Statistical analysis was by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test comparing samples exposed to a given concentration of NV716 with the corresponding control (no drug or ciprofloxacin alone): *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (B) Kinetics of killing of stationary-phase cultures of PAO1 (top) or PAO509 (bottom) by ciprofloxacin at 50× MIC alone or combined with NV716 at different concentrations. NV716 was added at different timings (0 h [left], 5 h [middle] or 24 h [right]), highlighted by the vertical dotted line and the arrow. All data are expressed as means ± SEM (triplicates from three experiments). (C) Killing of persister cells of PAO1 (left) or PAO509 (right) by ciprofloxacin, NV716, or their combinations. Persister cells were isolated after 5 h of incubation with ciprofloxacin at 50× MIC (persisters) and then incubated with either ciprofloxacin (CIP), NV716 at different concentrations, or their combination. All data are expressed as means ± SEM (triplicates from three experiments). Statistical analysis was by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test comparing samples exposed to CIP alone: *, P ≤ 0.05; ** P ≤ 0.01; ****, P ≤ 0.0001.