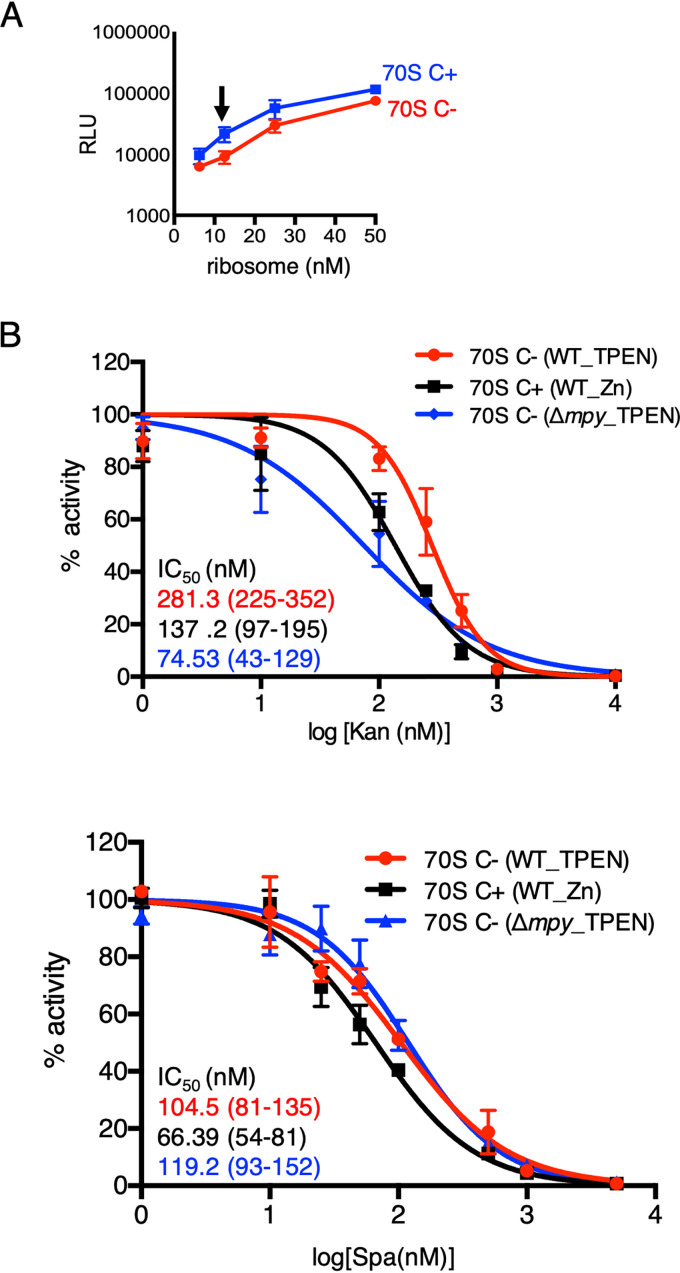
FIG 1.
MPY-independent decrease in Spa sensitivity of C− ribosomes of M. smegmatis. (A) Relationship between concentration and activity of C+ ribosomes purified from 96-h-old cultures of M. smegmatis in high-zinc (1 mM ZnSO4) Sauton’s medium (blue) or C− ribosomes purified from 96-h-old cultures of M. smegmatis in low-zinc (1 µM TPEN) Sauton’s medium (red). The activity was measured as relative luminescence units (RLU) of nano-luciferase synthesized in vitro in a transcription-translation coupled reaction. The arrow indicates the concentration (12.5 nM) selected for in vitro translation experiments shown in panel B and in the remainder of this paper. (B) Response of 12.5 nM wild-type (WT) C+, wild-type C−, and Δmpy C− ribosomes to indicated concentrations of Kan and Spa in an in vitro transcription-translation assay utilizing nano-luciferase described for panel A. While WT C+ ribosomes were purified from 96-h-old cultures in high-zinc Sauton’s medium, C− ribosomes from WT and Δmpy strains were purified from 96-h cultures in low-zinc Sauton’s medium. IC50 values (in colors corresponding to the plots) were obtained by GraphPad Prism from the variable slope of the nonlinear dose-response curve. Data represent two biologically independent experiments. Color-coded values in parenthesis denote 95% confidence intervals determined from the standard errors of the corresponding plots.