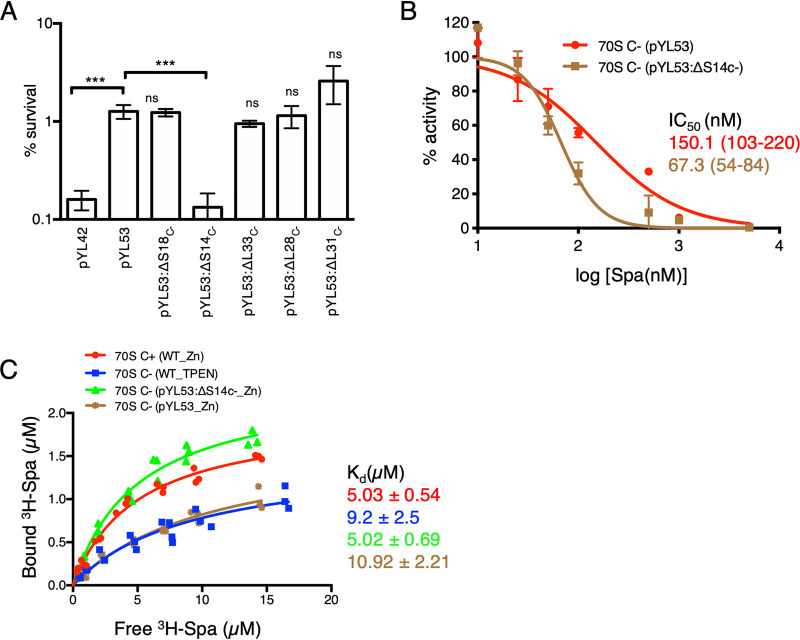
FIG 3.
S14C− is necessary and sufficient to reduce the Spa sensitivity of C− ribosomes. (A) Survival of the indicated strains of M. smegmatis after 4 days of Spa (50 µg/ml) exposure. The strain harboring pYL53 plasmid constitutively expressed C− ribosomes, while each of the others harboring pYL53-based plasmid with an in-frame deletion in the indicated gene of the c− operon expressed C− ribosomes without the corresponding protein. Protein compositions of 70S ribosomes from pYL53:ΔS14C− and pYL53:ΔS18C− strains were previously analyzed by mass spectrometry (8); those from pYL53:ΔL28C− and pYL53:ΔL33C− are shown in Fig. S2 in the supplemental material, confirming specific loss of the corresponding C− proteins. While incorporation of C+ counterparts of S18, L28, and L33 in the mutant ribosomes was also confirmed by the MS analysis, incorporation of S14C+ is implied from the fact that S14 is an essential protein for ribosome function. The strain harboring pYL42 and expressing C+ ribosomes was used as the control. Data represent means ± SDs from three biologically independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001 by t test; ns, not significant with respect to pYL53. (B) Spa sensitivity in vitro of ribosomes from high-zinc cultures of pYL53 and pYL53:ΔS14C− strains. The translation activity of 12.5 nM ribosomes was measured using a nano-luciferase assay and calculated as percent decrease from the activity measured in the absence of Spa. IC50 of Spa against each of the ribosomes (indicated with the corresponding colors) was determined as described for Fig. 1B. Data represent two biologically independent experiments. The values in parentheses denote 95% confidence intervals determined from the plots of corresponding colors. (C) Saturation binding plot of 3H-Spa to wild-type (WT) C+ and C− 70S ribosomes purified from low- and high-zinc cultures, respectively, as well as recombinant C− ribosomes purified from high-zinc cultures of pYL53 and pYL53:ΔS14C−. Kd values were determined from nonlinear regression curve fit (Y = Bmax × X/Kd + X) using GraphPad Prism. Three biologically independent preparations of each type of ribosomes were used.