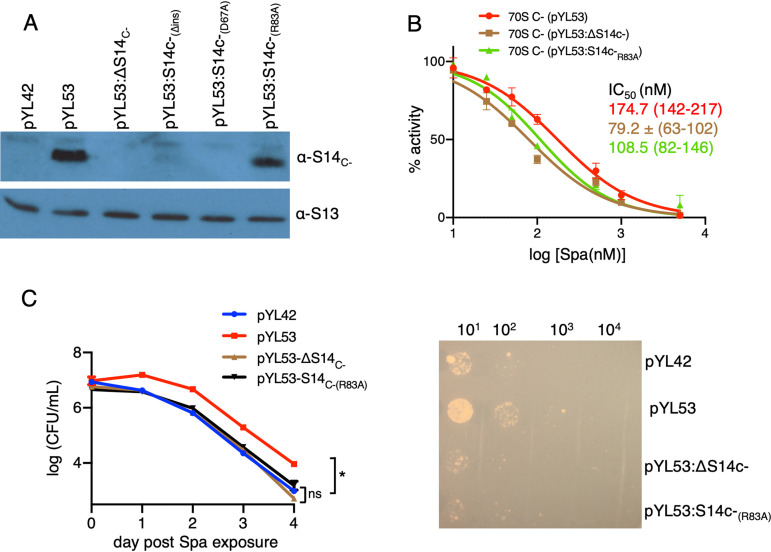
FIG 5.
The amino acid residue R83 of S14C− and Spa sensitivity of the C− ribosome. (A) Immunoblot analysis of recombinant C− ribosomes purified from high-zinc cultures of M. smegmatis strains constitutively expressing the c− operon from pYL53 or its derivatives carrying various mutations in S14C−; ΔS14C− denotes in-frame deletion, S14C−(Δins) denotes in-frame removal of the 40-aa-residue insertion, and S14C−(D67A) and S14C−(R83A) denote alanine substitutions at the respective residues. (B) Spa sensitivity in ribosomes from pYL53, pYL53:ΔS14C−, or pYL53:S14C−(R83A). Translation activities of ribosomes shown in panel B were measured using a nano-luciferase assay and calculated as percent decrease from the activity measured in the absence of Spa. IC50 of Spa against each of the ribosomes (indicated with the corresponding colors) was determined as described for Fig. 1B. Data from two biologically independent experiments were plotted. The values in parentheses denote 95% confidence intervals determined from the plots of corresponding colors. (C) Spa sensitivity in cells of the strains described for panel B. High-zinc cultures of these strains were inoculated in high-zinc Sauton’s medium containing 50 µg/ml of Spa and incubated for the indicated time periods prior to plating dilutions and enumerating colonies (after 3 days of incubation). Data represent means ± SDs from three biologically independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 by t test. A representative plate for 4-day time point is shown on the right.