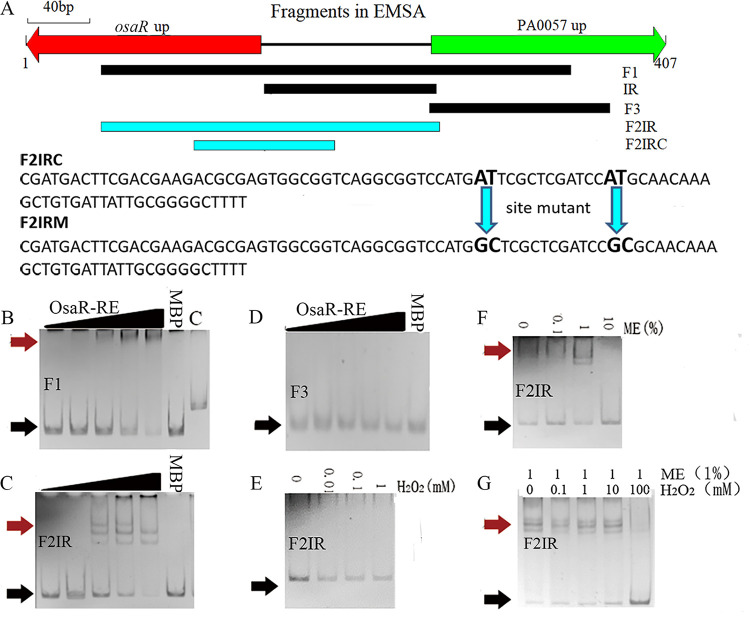
FIG 7.
Transcription factor binding properties of OsaR identified by EMSA analysis. (A) DNA fragments used in the EMSA analysis. (B to D) Validation of binding of OsaR-RE (with 1% ME) to selected target regions by EMSA. (E and F) Ability of the reduced state (OsaR-RE) (with ME) and the oxidized state (OsaR-OX) (with H2O2) to bind the target fragment at a protein concentration of 200 nM. (G) Reduction of OsaR (1000 nM) with 1% ME for 60 min followed by dialysis to remove ME in an anaerobic chamber. Oxidation of OsaR-RE was performed with various concentrations of H2O2 before application to the shift assay. DNA-protein complexes were separated upon migration on a native PAGE gel. OsaR was purified under aerobic conditions and used at the following concentrations: 0 nM, 50 nM, 100 nM, 200 nM, or 400 nM. The protein is a mixture of OsaR and MBP, because OsaR is unstable and easy to precipitate when more purification steps are performed after MBP is cut off. The proportion of OsaR was calculated using ImageJ software according to the SDS-PAGE picture. Red arrows indicate the protein-DNA complex and black arrows indicate free DNA. MBP (400 nM plus the DNA fragment) and C (OsaR-RE at 400 nM plus flpJG) are negative controls.