FIG 4.
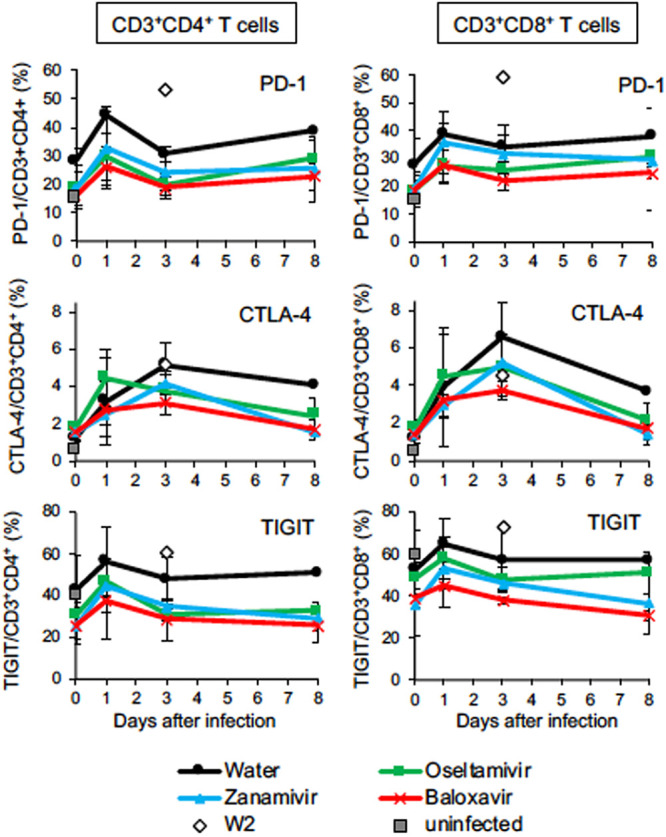
Percentages of T lymphocytes expressing immune checkpoint molecules during H7N9 HPAIV infection. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were collected from macaques infected with Dk/HE29-22 virus on days 0, 1, 3, and 8. The percentages of immune checkpoint molecule-positive cells in CD3/CD4-positive cells (left column) and CD3/CD8-positive cells (right column) are shown. Gates for analysis are shown in Fig. S5. Open diamonds, percentages of immune checkpoint molecule-positive cells in W2 at autopsy; gray squares, average percentages of immune checkpoint molecule-positive cells in uninfected macaques (n = 2). Averages and standard deviations for the results of three monkeys are shown, except that those in the DW group 4 to 8 days after virus inoculation are for two monkeys. There were no significant differences among the groups (P > 0.05; Mann-Whitney U test).
