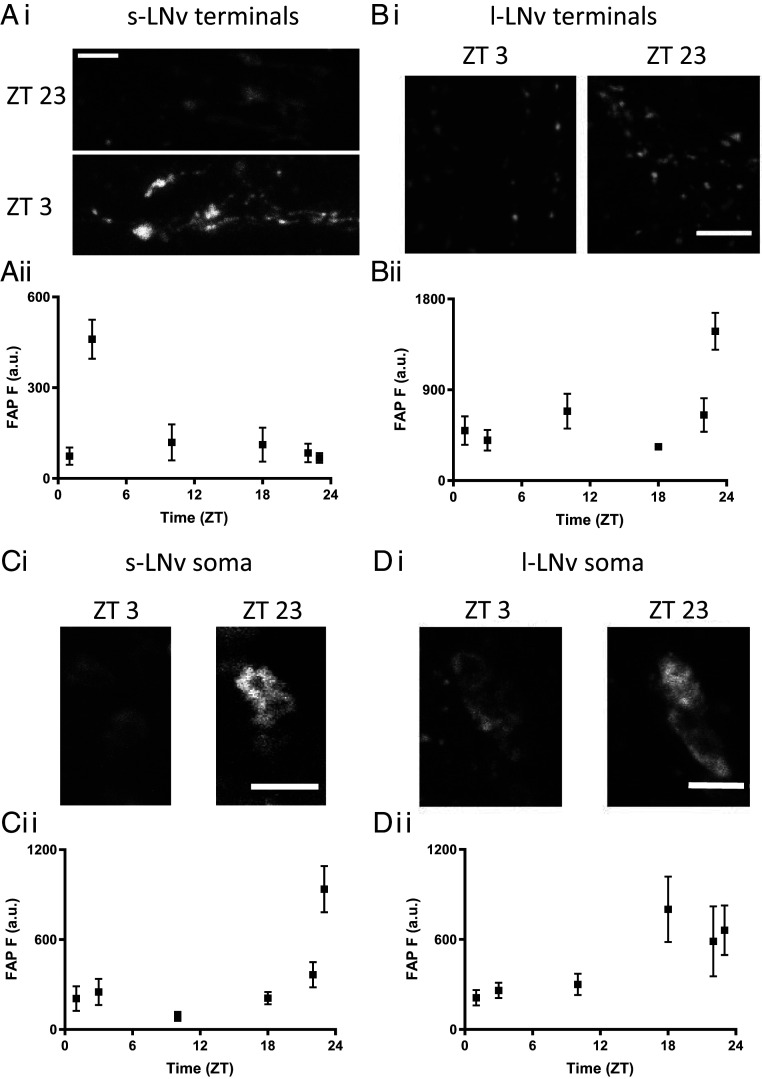
Fig. 1.
Multicompartmental neuropeptide release by two subsets of ventrolateral clock neurons exhibits daily rhythms. (Ai) FAP images of neuropeptide release at s-LNv terminals in UAS-Dilp2-FAP/UAS-Dilp2-GFP; Pdf-Gal4 flies at ZT3 and ZT23 in entrained flies (12L:12D) (Scale bar, 10 μm). (Aii) Quantification of neuropeptide release from s-LNv terminals. n = for time points ZT 1, 3, 10, 18, 22, and 23 are 10, 22, 5, 7, 7, and 7, respectively. (Bi) Images of neuropeptide release at l-LNv nerve terminals at ZT3 and ZT23 (Scale bar, 10 μm). (Bii) Quantification of neuropeptide release by l-LNv nerve terminals across the day and night. n = for time points ZT 1, 3, 10, 18, 22, and 23 are 13, 9, 8, 7, 10, and 8, respectively. (Ci) Imaging shows release at s-LNv somas at ZT3 and ZT23 in entrained flies (12L:12D) (Scale bar, 10 μm). (Cii) Quantification of neuropeptide release by s-LNv somas across the day and night; note the large spike in release occurring at the end of the night (12L:12D). n= for time points ZT 1, 3, 10, 18, 22, and 23 are 18, 11, 10, 13, 17, and 14, respectively. (Di) Images of neuropeptide release in l-LNv somas during the morning (ZT3) and late night (ZT23) (Scale bar, 10 μm). (Dii) Neuropeptide release by l-LNv somas across the day and night. n = for time points ZT 1, 3, 10, 18, 22, and 23 are 12, 13, 6, 9, 9, and 10, respectively.