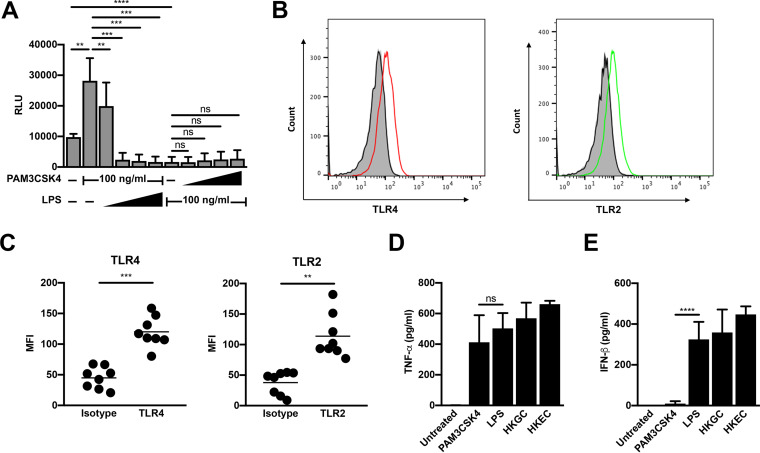
FIG 3.
TLR4 signaling is dominant in MDMs. (A) MDMs were infected with a single-round, replication-defective HIV-luciferase reporter virus and, 48 h after infection, were treated with a fixed concentration of PAM3CSK4 (100 ng/ml) and increasing concentrations of LPS (1 to 1,000 ng/ml, as indicated) or a fixed concentration of LPS (100 ng/ml) and increasing concentrations of PAM3CSK4 (1 to 1,000 ng/ml, as indicated) for 18 h. Cells were then lysed and assayed for luciferase activity. The data are the mean (± SD) of six donors; each donor was tested in triplicate. (B and C) At 8 days postisolation, MDMs were stained with antibodies against TLR2 or TLR4 or relevant isotype controls. Receptor expression was assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms from one representative donor are shown in panel B. Gray, unstained cells; black line, isotype control; red line, TLR4; green line, TLR2. Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) ± SD from eight donors is depicted in panel C. (D and E) MDMs were treated with the TLR2 ligand PAM3CSK4 (100 ng/ml), the TLR4 ligand LPS (100 ng/ml), heat-killed GC (MOI = 10), or heat-killed E. coli (MOI = 10) for 18 h. Cell supernatant was harvested, filtered through a 0.2-μm filter, and analyzed by enzyme-limited immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (D) and beta interferon (IFN-β) (E) production. Data represent mean (± SD) of seven donors (four donors for heat-killed E. coli). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.