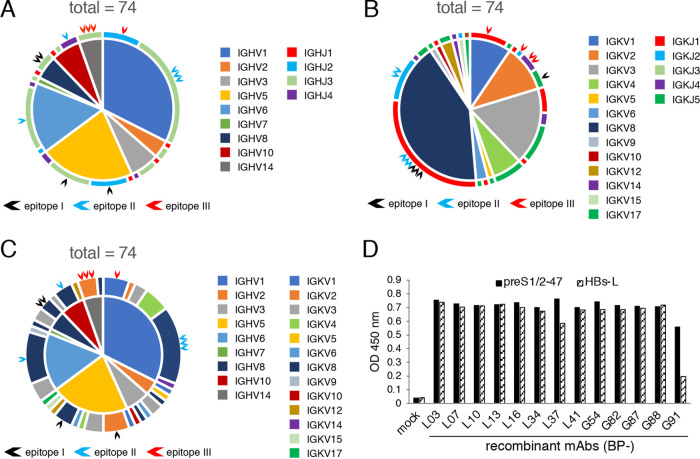
FIG 3.
Sequence analysis, expression, and epitope mapping of MAbs against preS1/2–47. cDNA sequences of VH and VL genes derived from preS1/2–47-specific memory B cells were analyzed by using IgBLAST. (A) Combinations of heavy chain V-J subgroups from 74 preS1/2–47 MAbs. The sections inside the circle represent the IGHV subgroups, and the outer circumference shows IGHJ subgroups. Black, blue, and red arrows indicate generated recombinant MAbs recognizing epitopes I, II, and III, respectively. (B) Combinations of light chain V-J combinations from 74 MAbs. The sections inside the circle represent the IGKV subgroups, and the outer circumference shows IGKJ subgroups. Black, blue, and red arrows indicate generated recombinant MAbs recognizing epitopes I, II, and III, respectively. (C) IGHV-IGKV combinations of 74 preS1/2–47 MAbs. The sections inside the circle represent the IGHV subgroup, and the outer circumference shows the IGKV subgroup. Black, blue, and red arrows indicate generated recombinant MAbs recognizing epitopes I, II, and III, respectively. (D) ELISA for binding of recombinant MAbs (1 μg/ml in PBS) to preS1/2–47 or HBs-L protein. OD, optical density. (E) Epitope mapping of preS1-specific recombinant MAbs. Forty-seven synthetic overlapping peptides of 10 to 20 amino acids corresponding to preS1/2–47 were used. The horizontal axis for each MAb shows absorbance units. The peptides showing antibody binding are marked by an asterisk. (F) Summary of minimum epitopes recognized by each MAb. The preS1/2–47 amino acid sequences used for immunization are shown. Yellow numbers in black bars represent the amino acid positions.