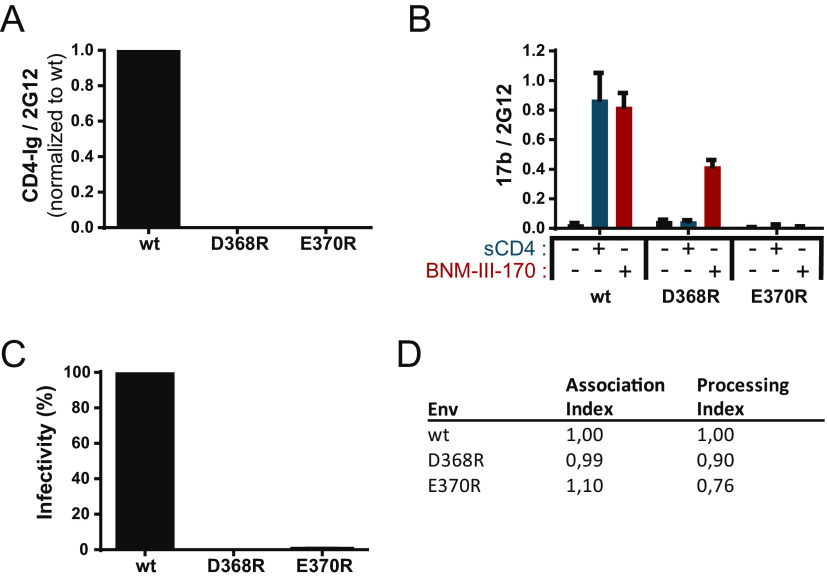
FIG 1.
CD4 binding site mutant characterization. (A and B) Recognition of Env-expressing cells by a cell-based ELISA using CD4-Ig (A) or 17b (B) in the presence or absence of sCD4 or the CD4mc BNM-III-170. Data shown represent mean relative light unit (RLU) values ± standard errors of the means (SEM) from at least three independent experiments performed in quadruplicate, with the signal obtained from cells transfected with an empty pcDNA3.1 plasmid (no Env) subtracted, normalized to Env levels as determined by bNAb 2G12. (C) Infectivity of Env variants compared to the wild type (wt). Reverse-transcriptase-normalized amounts of recombinant luciferase-expressing HIV-1 pseudotyped with the wt or the D368R or E370R mutant were used to infect Cf2Th-CD4/CCR5 cells at 37°C for 48 h. (D) The trimer stability of Env variants was measured by immunoprecipitation of radiolabeled Env and calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The association index measures the association of mutant gp120 with the Env complex on expressing cells relative to the wt, and the processing index measures proteolytic processing of the mutant gp160 Env precursor to mature gp120 relative to the wt. Results represent the mean values from three independent experiments.