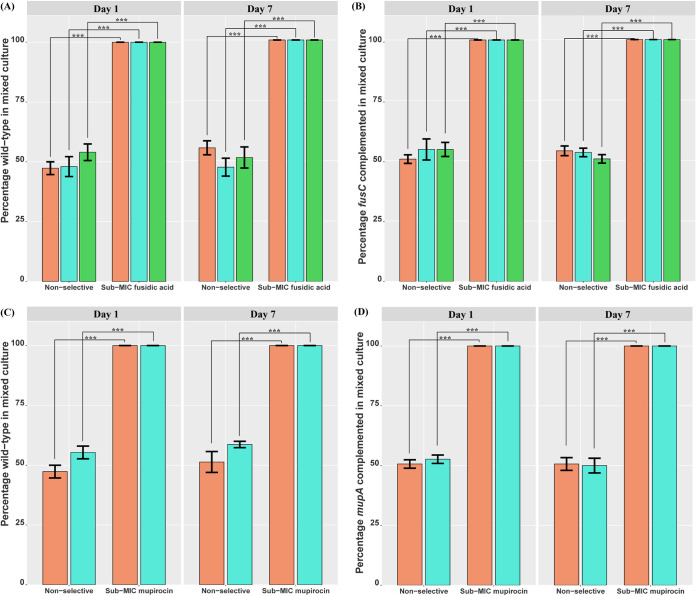
FIG 1.
In vitro competition assays of S. aureus reveal the selective advantage of topical antibiotic resistance gene carriage. S. aureus strains NZ14132 (orange), NZ14487 (aqua), and NZAK3 (green), wild-type or complemented strains, were paired with their respective isogenic mutants under nonselective conditions and exposure to a sub-MIC level of FA (0.03125 mg/liter) or mupirocin (0.125 mg/liter) for 7 days. (A to D) Percentages of wild-type or complemented isolates in mixed cultures of the wild type and fusC mutant (A), fusC complemented and fusC mutant (B), wild-type and mupA mutant (C), and mupA complemented and mupA mutant (D) strains were determined on days 1 and 7 postexposure. The mean percentages of three biological replicates are displayed for each condition tested, with black error bars representing the standard errors of the means (SEM). Statistically significant differences are indicated by asterisks (***, P < 0.001 by paired t test).