FIG 4.
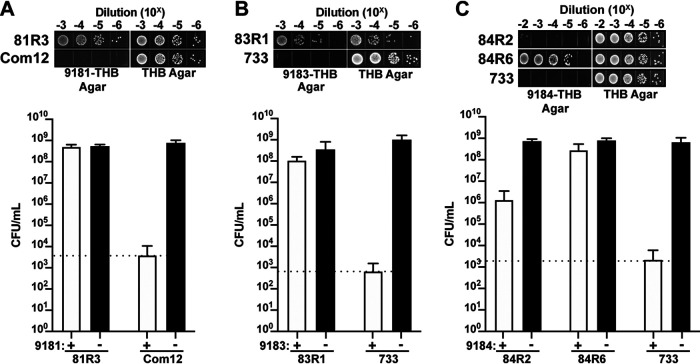
E. faecium elicits a robust resistance phenotype to phages 9181 and 9183 but variable resistance to phage 9184. (A to C) Representative phage-resistant strains raised against phages 9181 (A), 9183 (B), and 9184 (C). Data show phage susceptibility assays and associated bacterial enumeration of wild-type and phage-resistant mutants in the presence (white bars) or absence (black bars) of phages from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Phage 9181-resistant (A) and phage 9183-resistant (B) strains exhibit ≥4-log survival in the presence of phages compared to the parental E. faecium Com12 and 1,141,733 (733) strains, respectively. (C) Phage 9184-resistant strains exhibit diverse resistance strength characterized by weak (84R2) and strong (84R6) resistance phenotypes. The dotted line indicates the spontaneous mutation threshold of wild-type E. faecium, which is defined as the mean number of CFU per ml at which spontaneous phage resistance is observed for the wild-type host strain of each phage.