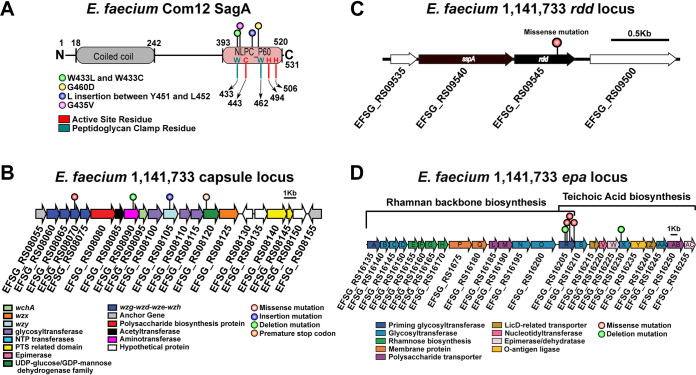
FIG 5.
Diverse assortment of mutations confers phage resistance in E. faecium. (A) Protein secondary structure of E. faecium Com12 SagA, consisting of an N-terminal coiled-coil domain (residues 18 to 242) and C-terminal NlpC_P60 peptidoglycan hydrolase domain (residues 393 to 520). Displayed above the protein structure are colored lollipops denoting the site of mutations within NlpC_P60 domain of phage 9181-resistant mutants. Inside and below the protein structure are colored one-letter amino acid abbreviations and lines, respectively, corresponding to key active-site (red) and peptidoglycan clamp (teal) residues of the NlpC_P60 domain. Abbreviations: W, tryptophan; C, cysteine; H, histidine; G, glycine; D, aspartate; L, leucine; Y, tyrosine; V, valine. (B) Capsule locus mutations are detected in a tyrosine kinase (wze), aminotransferase (efsg_rs08090), wzy (efsg_rs08105), and nucleotide sugar dehydrogenase (efsg_rs08120) of phage 9184-resistant mutants. Arrows indicate open reading frames. Arrow colors correspond to colored boxes (bottom left) and indicate predicted open reading frame function (17). Colored lollipops above the arrows corresponding to colored dots (figure bottom right) indicate the mutation type. E. faecium 1,141,733 locus tags are angled below the arrows. (C) A missense mutation is found within a predicted arginine-aspartate-aspartate protein (rdd; black arrow) of one phage 9184-resistant mutant (84R6) of E. faecium 1,141,733. rdd is flanked upstream by a predicted hypothetical protein (white arrow) and signal sequence peptidase A (sspA; black arrow) and downstream by another hypothetical protein (white arrow). E. faecium 1,141,733 locus tags are angled below the arrows. (D) Mutations in predicted teichoic acid biosynthesis genes (epaR and epaX) are identified in phage 9183-resistant mutants of E. faecium 1,141,733 (25). Arrow colors correspond to colored boxes (bottom left) and indicate predicted open reading frame function. Colored lollipops above the arrows corresponding to colored dots (bottom right) indicate the mutation type. E. faecium 1,141,733 locus tags are angled below the arrows. The brackets above the locus correspond the conserved (left) and variable (right) portions of the epa locus proposed by Gueredal et al. to encode the machinery necessary for rhamnopolysaccharide synthesis and wall teichoic acid biosynthesis, respectively (25).