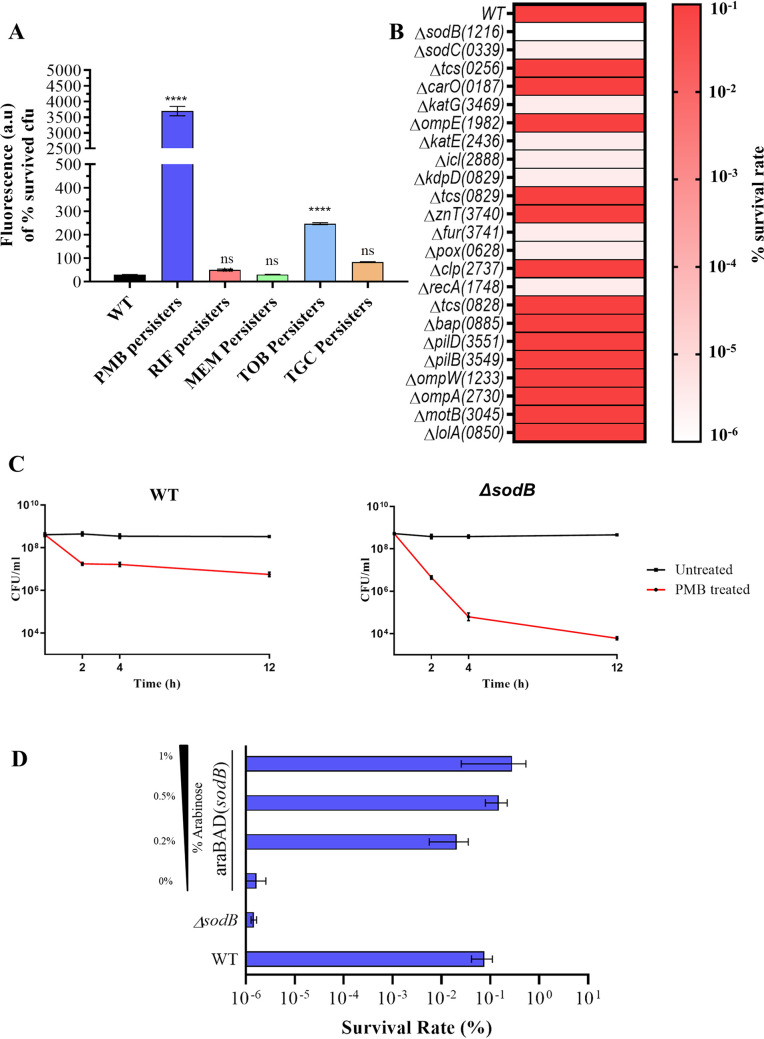
FIG 3.
Identification of the genes responsible for tolerance to polymyxin B in A. baumannii. (A) Measurement of ROS generation in A. baumannii persisters induced upon treatment with five antibiotics by using the ROS-sensitive fluorescent probe DCF-DA. (B) Heat map showing differences in polymyxin B tolerance in A. baumannii AB5075 mutants. Gene names are shown, with ABUW (i.e., gene locus ID of A. baumannii AB5075 strain) numbers in parentheses. The scale shows a gradient from 10−1 (dark orange) to 10−6 (white). (C) Biphasic killing curve showing differences in persister survival rates between wild-type and sodB mutant A. baumannii AB5075 cells upon treatment with 10× MIC of polymyxin B. (D) Complementation of araC-sodB in the A. baumannii AB5075 ΔsodB strain, resulting in restoration of polymyxin B tolerance. WT, wild-type; PMB, polymyxin B; RIF, rifampicin; MEM, meropenem; TOB. tobramycin; TGC, tigecycline. ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.