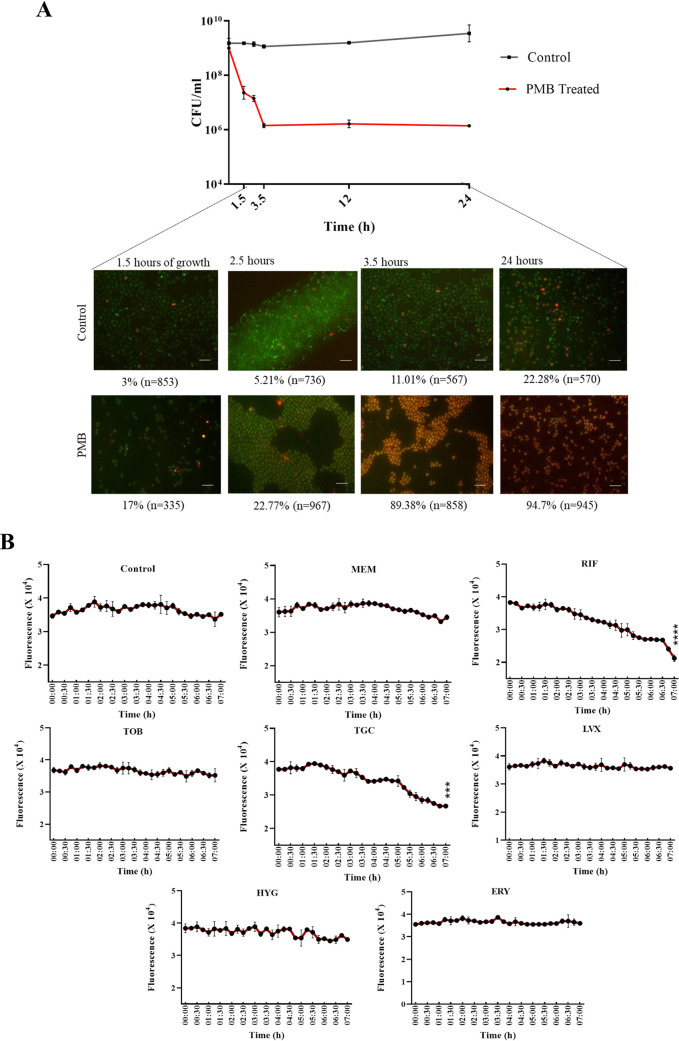
FIG 4.
Dual fluorescent module in A. baumannii for identification of antibiotics to effectively kill polymyxin B-induced A. baumannii persisters. (A) Cells were harvested at different time points, including early exponential phase, late exponential phase, early stationary phase, and late stationary phase. Upon treatment with 10× MIC of polymyxin B, cells were harvested at treatment times ranging from 1.5 h to 24 h. Scale bar for all images, 50 μm. (B) Polymyxin B-induced persisters with the dual fluorescence module of A. baumannii AB5075 were treated with seven antibiotics at concentrations below the clinical breakpoint concentration. Survival kinetics of persisters upon treatment were monitored by taking fluorescence readings of red-fluorescing cells. MICs were as follows: meropenem, 4 μg/ml; rifampicin, 1 μg/ml; tobramycin, 8 μg/ml; tigecycline, 0.5 μg/ml; hygromycin, 16 μg/ml; levofloxacin, 2 μg/ml; erythromycin, 8 μg/ml. PMB, polymyxin B; MEM, meropenem; RIF, rifampicin; TOB. tobramycin; TGC, tigecycline; HYG, hygromycin; LVX, levofloxacin; ERY, erythromycin,. Each treatment group was compared with the control group for statistical significance. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001.