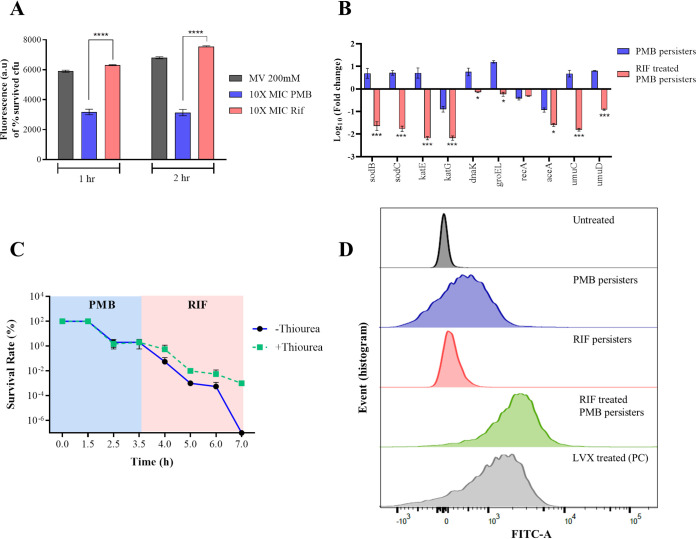
FIG 5.
Suppression of sodB leads to enhanced ROS generation and eradication of polymyxin B-induced A. baumannii persisters. (A) Time-dependent increase in ROS generation upon rifampicin treatment measured using the ROS-sensitive fluorescent probe DCF-DA. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of ROS-scavenging genes in A. baumannii. Relative gene expression was calculated by the ΔΔCT method, using 16S rRNA as the reference genes. (C) ROS quenching by using thiourea conferring protection of polymyxin B-induced A. baumannii persisters upon rifampicin treatment, suggesting that ROS-mediated killing is the sole mechanism of persisters eradication. (D) TUNEL assay coupled with flow cytometry to assess rifampicin treatment-induced DNA damage in A. baumannii persisters. The x axis represents the relative FITC fluorescence. MV, methyl viologen; PMB, polymyxin B; Rif, rifampicin; LVX, levofloxacin; PC, positive control; ****, P < 0.0001.