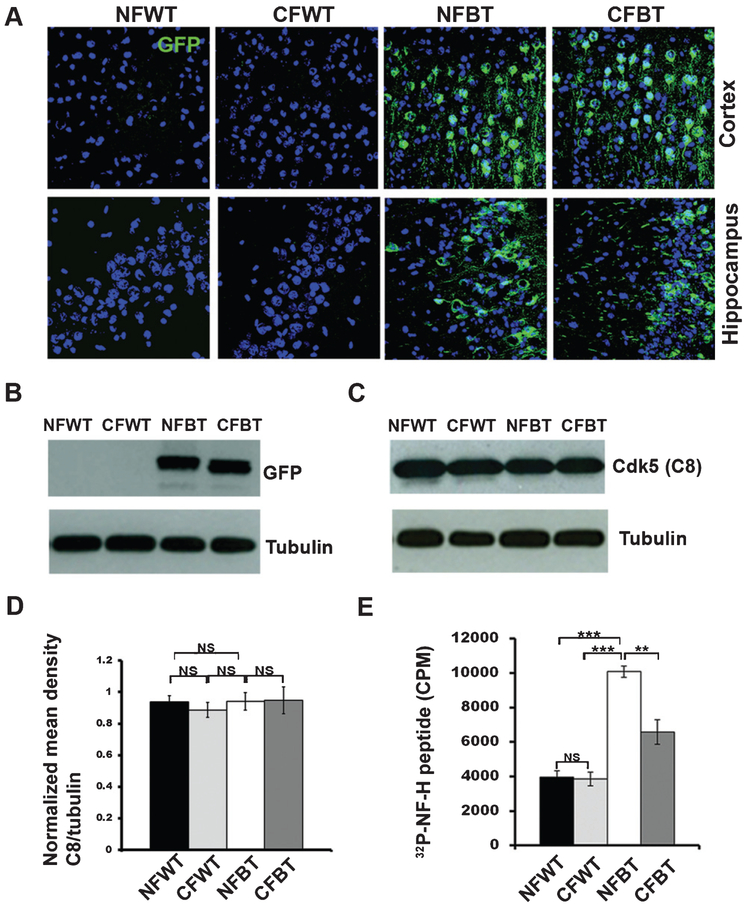
Fig. 1.
Expression and activity levels of Cdk5 in curcumin-treated p25Tg mice. A) Confocal images (from the cortex (layer 2/3) (top panels) and hippocampus (CA3 region) (bottom panels) of the brain sections and from 18-week-old wild type mice with normal feed (NFWT), wild type mice with curcumin feed (CFWT), 12-week induced (18-week-old) p25Tg mice with normal feed (NFBT), and p25Tg mice with curcumin feed (CFBT) using anti-GFP antibody (n = 3). Scale bars represent 20 μm. B) Immunoblot analyses results of brain lysates from the samples same as in (A) using anti-GFP antibody (n = 3). C) Western blot analyses results of brain lysates from 12-week induced p25Tg/control mice with/without curcumin treatment using anti-C8 antibodies (n = 3). D) Quantification of C8 immunoblots in C by densitometric scanning (NS p > 0.05). E) Kinase assay results of the brain lysates from the samples same as in A (n = 3) (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and NS p > 0.05) (one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test). Error bars indicate ± s.e.m.