Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Morris water maze-associated neurons are reactivated during the Morris water maze but not during fear conditioning.
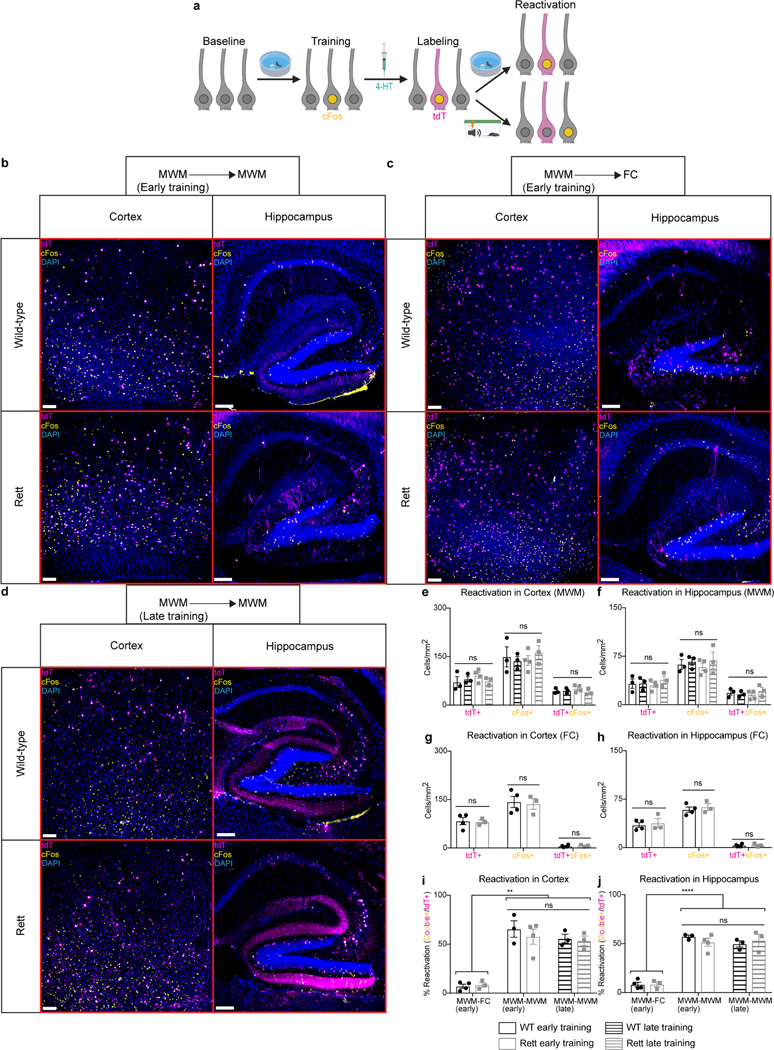
a, FosTRAP labeling of Morris water maze-associated neurons, with subsequent reactivation of task-specific neurons during retesting in the Morris water maze or fear conditioning assay. b-j, cFos reactivation in Morris water maze (MWM)-associated neurons of early-trained mice retested in the Morris water maze (b), early-trained mice tested in a novel fear conditioning (FC) assay (c), and late-trained mice retested in the Morris water maze (d) at 13 weeks of age. The number of tdTomato+ (tdT+), cFos+, and tdT+cFos+ neurons were quantified in the cortex (e) and hippocampus (f) of early-trained WT (n = 3) and Rett (n = 4) mice and late-trained WT (n = 3) and Rett (n = 3) mice after retesting in the Morris water maze. The number of tdTomato+ (tdT+), cFos+, and tdT+cFos+ neurons were quantified in the cortex (g) and hippocampus (h) of early-trained WT (n = 4) and Rett (n = 3) mice after fear conditioning. The reactivation percentage, defined as the percentage of tdT+ neurons that were also cFos+, were quantified in the cortex (i) and hippocampus (j) of Morris water maze-trained mice after retesting in the Morris water maze or the fear conditioning assay. Scale bar, 200 μm. The sample size (n) corresponds to the number of biologically independent mice. 3–4 sections were analyzed per mouse. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; ns (p>0.05), ** (p<0.01), **** (p<0.0001).
