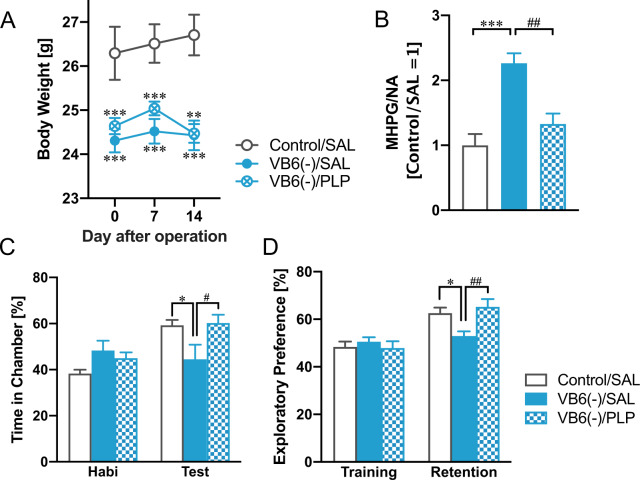
Fig. 4. Rescue of behavioral deficits in VB6-deficient mice by PLP supplementation into the brain.
A Changes in body weight after the implantation of osmotic pump are shown (Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures: FInteraction(4,50) = 2.38, p > 0.05; FDay(2,50) = 3.31, p < 0.05; FGroup(2,25) = 11.6, p < 0.05. B NA turnover in the PFC were determined by HPLC. One-way ANOVA: F(2,25) = 15.7, p < 0.001. C Exploratory preference in the novel object recognition test and D time spent in the chamber in the social interaction test were measured. Two-way ANOVA: C FInteraction(2,25) = 6.10, p < 0.01; FSession(1,25) = 38.0, p < 0.001; FGroup(2,25) = 1.67, p > 0.05, D FInteraction(2,25) = 7.67, p < 0.01; FSession(1,25) = 16.5, p < 0.001; FGroup(2,25) = 1.16, p > 0.05. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (vs. control/SAL) and #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 (vs. VB6(−)/SAL) using Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (n = 9–10). The data were shown as mean ± SEM values.