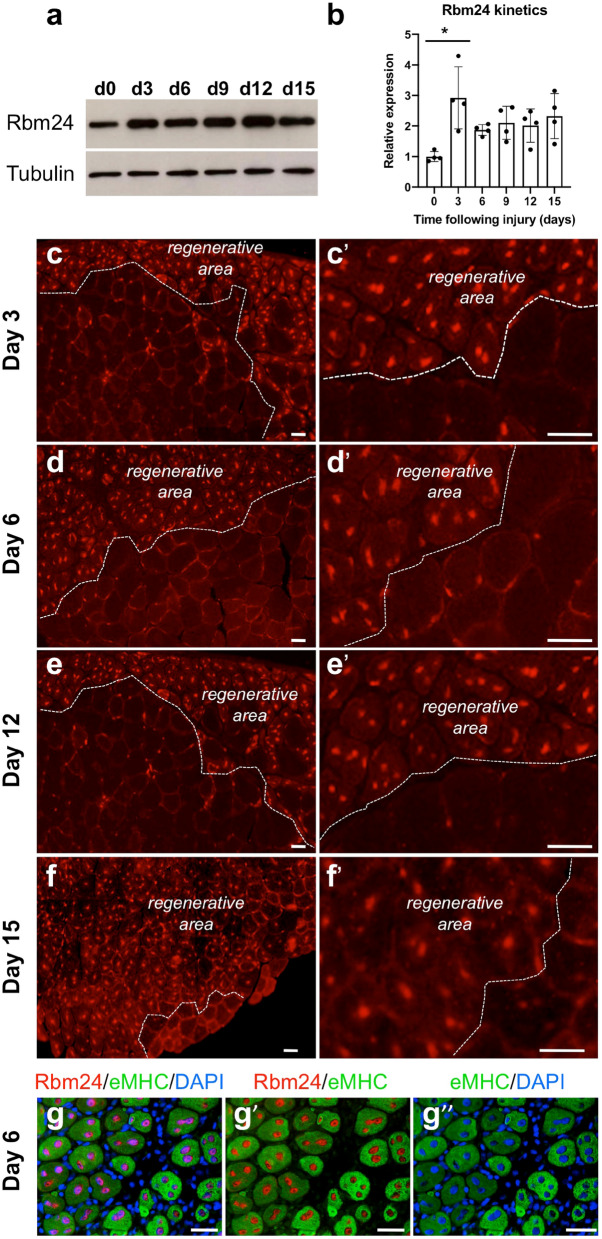
Figure 3.
Rbm24 expression during skeletal muscle regeneration in mice. (a) Western blot analysis of Rbm24 protein in the tibialis anterior muscle of adult mice at 3, 6, 9, 12 and 15 days of regeneration. Control muscle was the contralateral tibialis anterior injected with PBS. Tubulin was used as a loading control. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S2. (b) Quantification of Rbm24 protein levels followed by ANOVA analysis shows increased expression of Rbm24 after muscle injury. Rbm24 protein level in control muscle harvested at day 0 is set to 1 as a reference, after normalization with tubulin. Data are the mean ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments. ANOVA F (df 5.18) = 4.247, p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 by Tukey’s HSD test. (c–f′) Immunofluorescence staining on cryosections of mouse adult tibialis anterior muscle at 3, 6, 12 and 15 days of regeneration shows increased expression of Rbm24 in the nucleus of regenerating myofibers. For all time points, low (left panel) and higher (right panel) magnifications are shown. White dotted lines delimit regenerating areas composed of newly formed myofibers with centralized nuclei and uninjured myofibers with peripheral nuclei. (g–g″) Double immunofluorescence staining of Rbm24 and eMHC proteins in the tibialis anterior at 6 days of regeneration. As the first myosin isoform expressed in developing muscle fibers, eMHC is re-expressed at early stages of muscle regeneration. DAPI was used to stain nuclei. Rbm24 protein is localized in centralized nuclei of newly formed myofibers that repair the injured muscle tissue, but not in nuclei outside the myofibers. Scale bars: 10 µm.