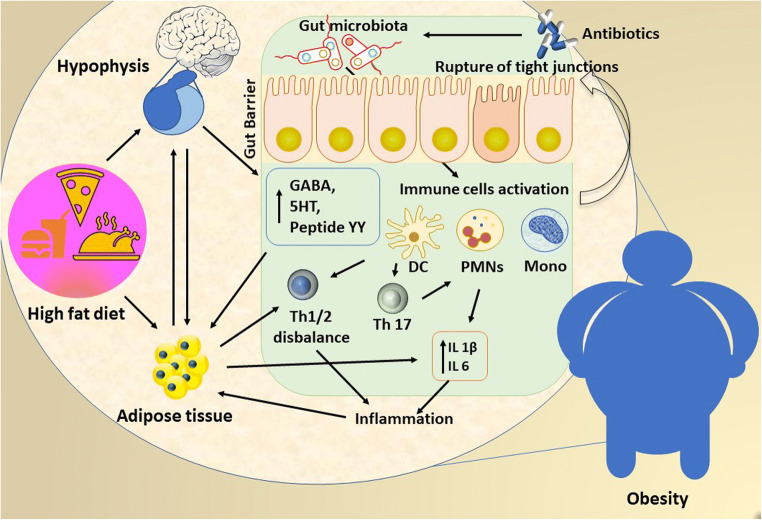
Fig. 2.
Gut dysbiosis triggered by environmental exposures such as diet and antibiotics plays an important role in disrupting molecular metabolism and impacting on obesity outcomes. In obesity, the adipose tissue is infiltrated with inflammatory immune cells that produce high amounts of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The gut barrier is disrupted causing gut antigens and PAMPs such as LPS to enter the tissue and stimulate inflammation. DC: dendritic cells, GABA: gamma aminobutyric acid, Mono: monocytes, PYY: peptide YY, PMNs: polymorphonuclear neutrophils, Th: T helper cells; 5HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine