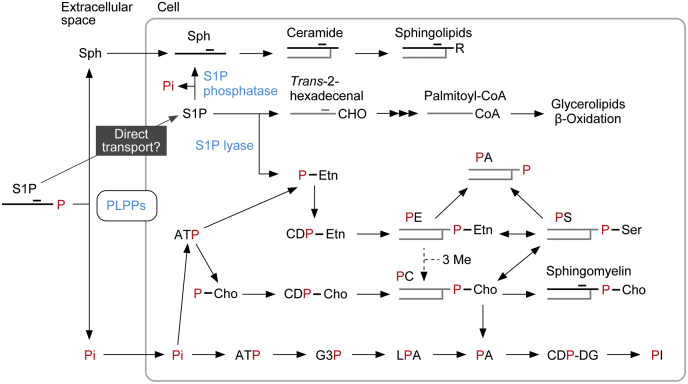
Figure 1.
S1P metabolic pathway. The phosphate (P) group of S1P is illustrated in red, and lipids containing red P can be radiolabeled by [32P]S1P. S1P transported directly into cells is dephosphorylated by S1P phosphatases or cleaved by S1P lyase. The former reaction produces Sph, and the latter reaction produces trans-2-hexadecenal and phosphoethanolamine. Sph is metabolized to complex sphingolipids via ceramide. Trans-2-hexadecenal is metabolized to palmitoyl-CoA via trans-2-hexadecenoic acid and trans-2-hexadecenoyl-CoA and then subjected to lipid synthesis (mainly glycerolipids) or β-oxidation. Phosphoethanolamine is metabolized to PE via CDP-ethanolamine. PE can be converted to PS through a base-exchange reaction, and a fraction of the PS generated is further converted to PC through another base-exchange reaction. Alternatively, PE can be metabolized to PC by receiving three methyl groups, a reaction that occurs in the liver (18). A fraction of PC is used in a sphingomyelin-producing reaction, where phosphocholine is transferred to ceramide (52). Some of the PE and PC are degraded by phospholipase D to PA. Most extracellular S1P is dephosphorylated by PLPPs, generating Pi and Sph. Sph is rapidly imported into cells and metabolized to ceramides and then further to complex sphingolipids. After being transported into cells, Pi is converted to ATP, and then to phosphoethanolamine, phosphocholine, or glycerol 3-phosphate, followed by metabolism to glycerophospholipids. Cho, choline; CHO, aldehyde group; DG, diacylglycerol; Etn, ethanolamine; G3P, glycerol 3-phosphate; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; Me, methyl group; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; P-Cho, phosphocholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; P-Etn, phosphoethanolamine; Pi, orthophosphoric acid; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PLPP, phospholipid phosphatase; PS, phosphatidylserine; R, polar group; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; Sph, sphingosine.