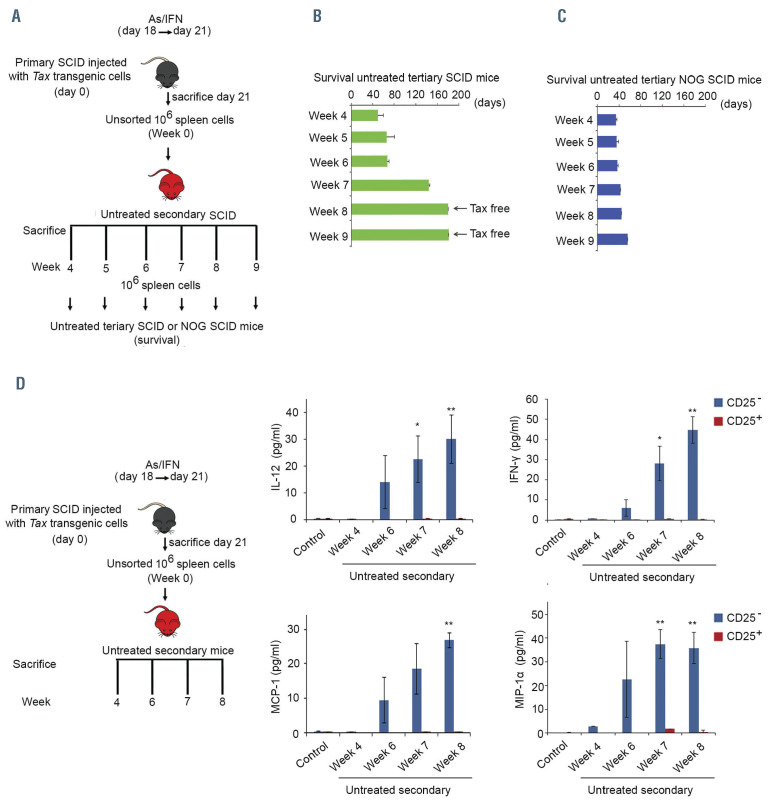
Figure 4.
Loss of leukemia-initiating cell activity requires innate immunity. (A) Primary mice injected with cells, derived from the tumoral spleen of tax transgenic mice that developed adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL), were treated with arsenic trioxide (AS) and interferon alpha (IFN) for 3 days then sacrificed. One million unsorted spleen-derived cells were injected into 50 secondary SCID mice that were left untreated and sacrificed on a weekly basis (5 per week). (B, C) One million unsorted spleen cells derived from weekly sacrificed untreated secondary SCID mice were injected into tertiary SCID (green histograms) (B) or NOG SCID (dark blue histograms) (n=10/condition) (C) mice that were left untreated. (D) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay on supernatant of homogenized spleen-derived CD25+ and CD25– sorted cells from weekly sacrificed untreated secondary mice injected with 106 unsorted spleen cells from AS/IFNα-treated primary mice. Control indicates secondary mice injected with 106 unsorted spleen cells from untreated primary mice. The t-test was performed to validate significance. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, and ***P≤0.001. P-values ≤0.05 were considered statistically significant.