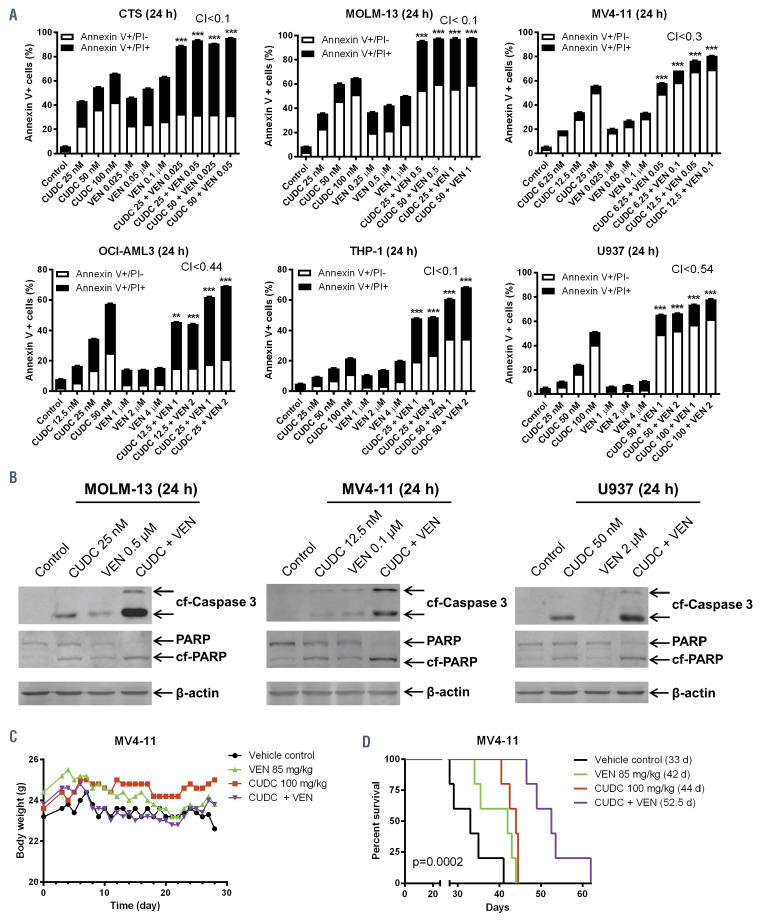
Figure 1.
CUDC-907 and venetoclax synergistically induce apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells in vitro and show in vivo efficacy in an acute myeloid leukemia cell line derived xenograft mouse model. (A) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines were treated with vehicle control, venetoclax (VEN), CUDC-907 (CUDC), or in combination for 24 hours. Annexin V-FITC/PI staining was assessed by flow cytometry analysis. Mean percent Annexin V+ cells ± standard error of the mean are shown. Combination index (CI) values were calculated using CompuSyn software. ***P<0.001 compared to individual drug treatment. (B) AML cells were treated with CUDC-907 and venetoclax, alone or in combination, for 24 hours. Whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting and probed with anti-cleaved caspase 3 (cf-Caspase 3), -PARP (cf-PARP indicated cleaved PARP), or –b-actin antibody. (C) MV4-11 cells (1x106 cells/mouse) were injected intravenously through the tail vein of immunocompromised NSGS mice. Three days post cell injection the mice were randomized (5 mice/group) and treated with vehicle control (3% 200 proof ethanol, 1% polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monooleate, and USP water), 85 mg/kg/inj venetoclax, 100 mg/kg/inj CUDC-907, or 85 mg/kg/inj venetoclax plus 100 mg/kg/inj CUDC-907 daily. The mice were treated for 8 consecutive days followed by 4 days off and then an additional 6 days. Body weight was measured on a daily basis and are graphed as mean ± standard error of the mean (panel C). Overall survival probability, estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method, is shown (panel D).