Figure 3.
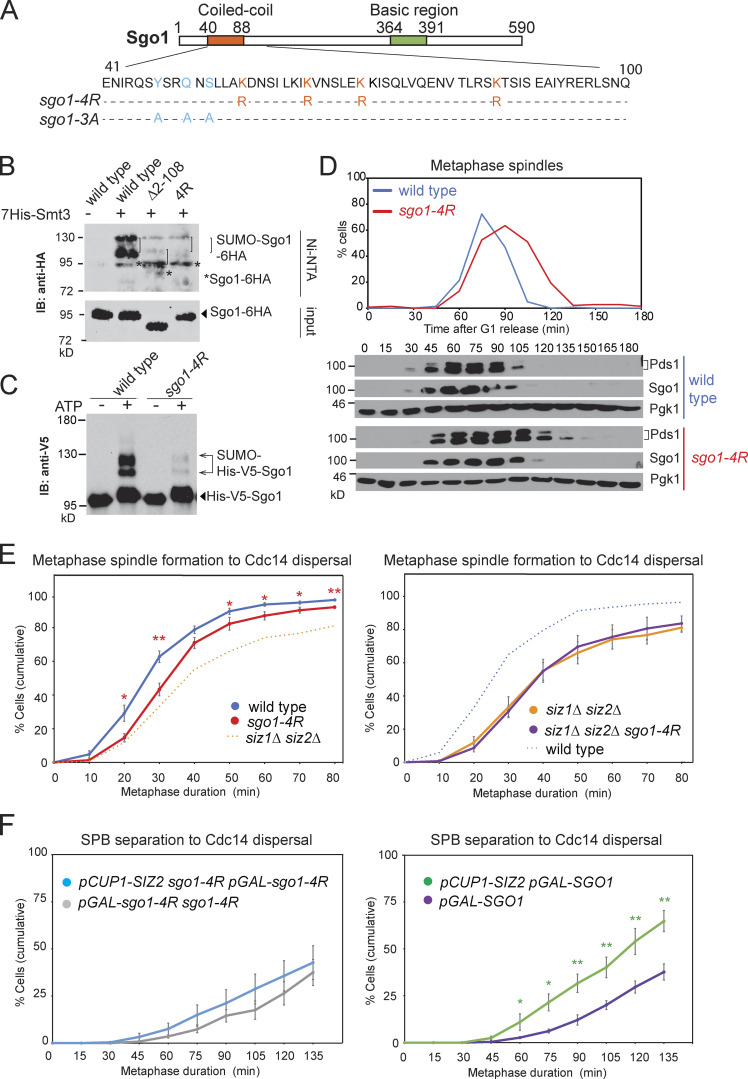
Sgo1 SUMOylation requires residues within its coiled coil and is important for timely anaphase onset. (A) Schematic of Sgo1 showing the sequence of the coiled-coil domain (bottom) and residues mutated in the indicated mutants. (B) Sgo1 SUMOylation requires residues in the coiled-coil domain. Strains for in vivo SUMOylation analysis carried Sgo1-6HA and were wild-type (AMy7655), sgo1-Δ2-108 (AMy14764), and sgo1-K56R K64R K70R K85R (‘4R’, AMy21898). IB, immunoblot. (C) Sgo1-4R shows reduced SUMOylation in vitro. Purified Sgo1 and Sgo1-4R proteins were SUMOylated in vitro using 0.1 µM E1–E3, in the presence or absence of ATP. (D) The sgo1-4R mutant is delayed in metaphase. Cell cycle analysis of wild-type (AMy8467) and sgo1-K56R K64R K70R K85R-9Myc (AMy23934) strains carrying SGO1-9MYC and PDS1-3HA was performed as described in Fig. 1 D. (E) Metaphase duration was measured after live-cell imaging of wild-type (AMy24174), siz1Δ siz2Δ (AMy24313), sgo1-4R (AMy29305), and sgo1-4R siz1Δ siz2Δ (AMy29297) strains carrying YFP-TUB1 and CDC14-GFP as described in Fig. 1, E and F. Shown are the average values of five independent experiments. Error bars represent standard errors. Statistics: one-tailed Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). (F) Overexpression of SIZ2 does not effectively rescue sgo1-4R overexpression. sgo1-4R pGAL-sgo1-4R (AMy29525), sgo1-4R pGAL-sgo1-4R pCUP1-SIZ2 (AMy29524), and pGAL-SGO1 (AMy27596) and pGAL-SGO1 pCUP1-SIZ2 (AMy27738) strains carried Spc42-tdTOMATO and Cdc14-GFP. The experiment was performed as described in Fig. 1, B and C. Shown are the average values of five independent experiments. Error bars represent standard errors. Statistics: one-tailed Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).