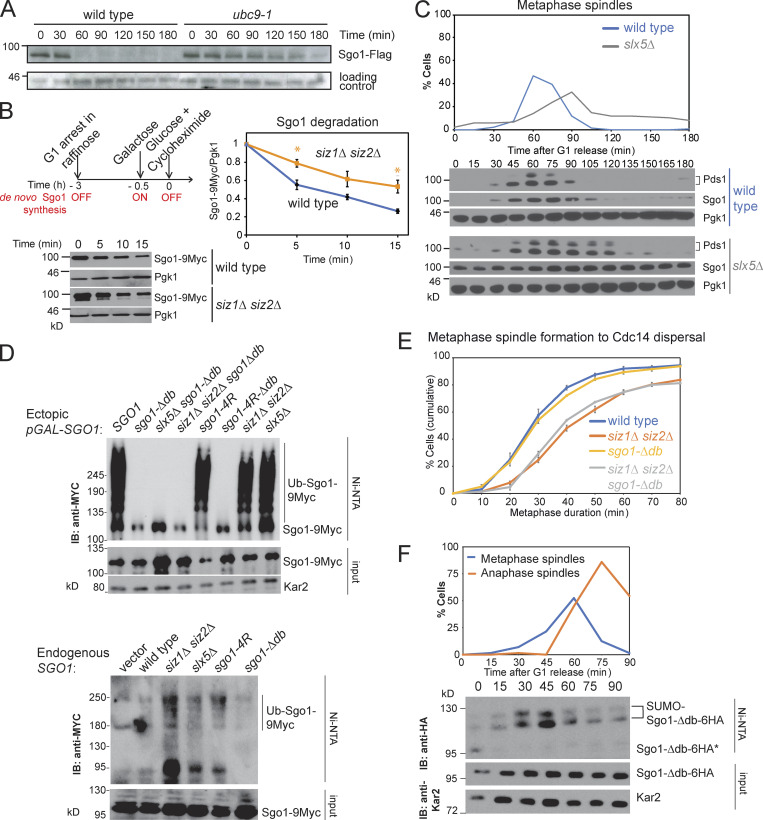
Figure 4.
Analysis of factors promoting Sgo1 degradation. (A) The degradation of Sgo1 depends on SUMO-conjugating protein Ubc9. Wild-type and ubc9-1 cells were synchronized in nocodazole and released into medium with α-factor to ensure arrest in G1. (B) Siz1/Siz2 promote Sgo1 degradation. Cycloheximide pulse chase experiment was performed for pGAL-SGO1-9MYC (AMy1392) and siz1Δ siz2Δ pGAL-SGO1-9MYC (AMy22584). As described in the scheme, cells were arrested in G1 throughout the experiment, and pGAL1-SGO1-9MYC expression was initially prevented by growth of cells in raffinose. Subsequently, a pulse of Sgo1 was provided by the addition of galactose, after which de novo Sgo1-9Myc synthesis was quenched by the addition of glucose (to block pGAL expression) and cycloheximide (to block protein synthesis). Representative anti-Myc and anti-Pgk1 (loading control) immunoblots are shown. Signal intensity was quantified using ImageJ. Relative Sgo1 levels were calculated as the ratio of Myc signal to Pgk1 signal, and the ratio was set to 1 for time 0. Shown is the average from three independent experiments, and error bars represent standard error. Statistics: one-tailed Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05). (C) slx5Δ cells exhibit a metaphase delay and stabilize Sgo1. Wild-type (AMy8467) and slx5Δ (AMy10981) strains carrying PDS1-3HA and SGO1-9MYC were analyzed as described in Fig. 1 D. (D) Sgo1 ubiquitination is dependent on its destruction box and independent of Sgo1 SUMOylation or Slx5/Slx8. Top: Strains with pGAL-SGO1-9MYC (AMy27029), pGAL-sgo1-Δdb-9MYC (AMy27030), slx5Δ pGAL-sgo1-Δdb-9MYC (AMy27031), siz1Δ siz2Δ pGAL-sgo1-Δdb-9MYC (AMy27032), pGAL-sgo1-4R-9MYC (AMy27033), pGAL-sgo1-4R-Δdb-9MYC (AMy27034), siz1Δ siz2Δ pGAL-SGO1-9MYC (AMy27035), and slx5Δ pGAL-SGO1-9MYC (AMy27036) and carrying His-UBI (AMp1673) were arrested in G1 in 2% raffinose and Sgo1 overexpression was induced by the addition of 2% galactose. Bottom: Cycling cells of the following strains: SGO1-9MYC (AMy29604), siz1Δ siz2Δ SGO1-9MYC (AMy29521), slx5Δ SGO1-9MYC (AMy29519), sgo1-4R-9MYC (AMy29632), and sgo1-Δdb-9MYC (AMy29662) carrying His-Ub (AMp1568) or empty vector were analyzed. Ubiquitinated proteins were purified on Ni-NTA resin and Sgo1-9Myc was detected in inputs and elutes by anti-Myc immunoblot (IB). (E) Preventing Sgo1 degradation is not sufficient to delay timely anaphase entry. Wild-type (AMy24174), siz1Δ siz2Δ (AMy24313), sgo1-Δdb (AMy29483), and siz1Δ siz2Δ sgo1-Δdb (AMy29484) carried CDC14-GFP and YFP-TUB1. Metaphase duration was determined as described in Fig. 1, E and F. Shown are the average values of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard errors. (F) Like wild-type Sgo1, Sgo1-Δdb is SUMOylated maximally in prometaphase. Sgo1-Δdb-6HA (AMy18191) carried His-SMT3 and was released from G1 arrest. Samples were harvested at the indicated time intervals for anti-tubulin immunofluorescence (top) and SUMO pull-down.