Figure 4.
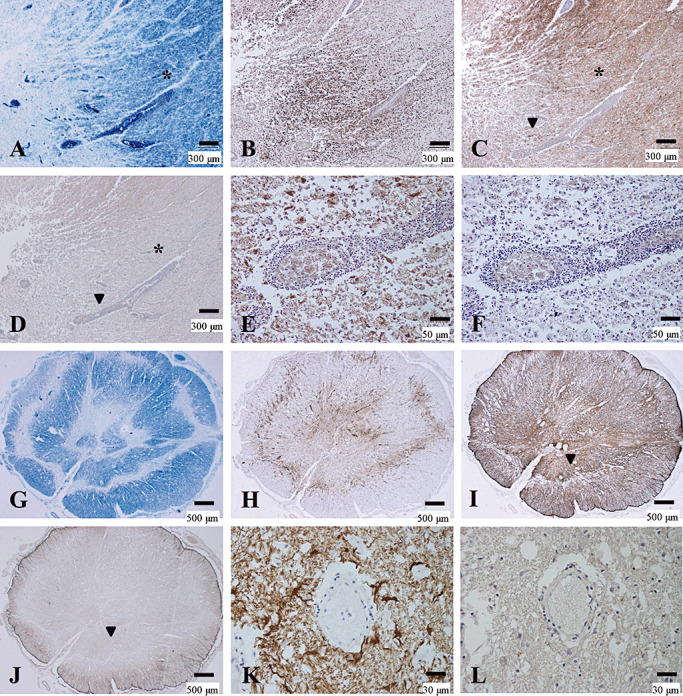
Preferential loss of AQP4 immunoreactivity in MS. (A–F) Serial sections of actively demyelinating lesions in the midbrain of MS‐3 without optic‐spinal lesions representing Patterns A & N. A. A demyelinating plaque in the acute stage in the cerebral peduncle, with dense perivascular lymphocytic cuffing. Myelin is still preserved at the periphery of the lesion (asterisk) despite CD68‐positive foamy macrophage infiltration (B). C. GFAP immunoreactivity is decreased in the lesion center while numerous reactive astrocytes are present at the lesion edge and surrounding areas (asterisk). D. AQP4 immunoreactivity is extensively lost in not only the demyelinating center but also in the surrounding areas, where GFAP immunoreactivity is preserved (asterisk). E. High magnification of the area indicated by an arrowhead in C and D. Vascular foot processes are destroyed but there are remaining GFAP‐positive astrocytes. F. The same microscopic field as in E. Astrocytes are devoid of AQP4 immunoreactivity. (G–L) Serial sections of chronic active Baló‐like concentric lesions in the spinal cord from MS‐4 representing Pattern A. G. The spinal cord shows concentric bands of alternating demyelination and preserved myelin. H. CD68‐positive macrophages are still abundant in the lesions. I. GFAP immunostaining indicates strong gliosis at the lesion edge and surrounding areas. J. AQP4 immunoreactivity is completely lost in the lesion center and the surrounding area with preserved myelin staining (note the AQP4‐immunopositive area only at the periphery of the spinal cord). K. High magnification of the blood vessels indicated by the arrowhead in I and J shows numerous GFAP‐positive reactive astrocytes and remnant astrocytic vascular foot processes. L. In the same area as K, AQP4 immunoreactivity is completely lost in the GFAP‐positive structures. A, G, KB; B, H, CD68 immunohistochemistry (IHC); C, E, I, K, GFAP IHC; D, F, J, L, AQP4 IHC. Scale bar = 500 µm (G–J); 300 µm (A–D); 50 µm (E, F); 30 µm (K, L). AQP4 = aquaporin‐4; GFAP = glial fibrillary acidic protein; KB = Klüver‐Barrera staining; MS = multiple sclerosis.
