Figure 5.
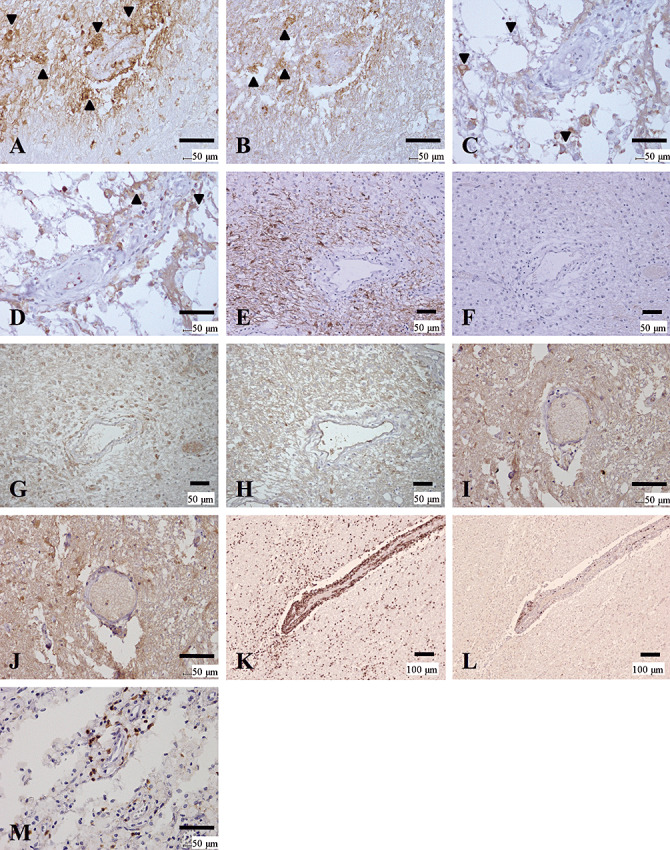
Distinctive patterns of perivascular immunoglobulin/complement deposition and lymphocytic cuffing between NMO and MS. (A–D) Active lesions in NMO with immunoglobulin/complement deposition. (A, B) Serial sections of a periplaque, still‐myelinated area of NMO‐4. These figures show the same area as that indicated by the arrowhead in Figure 1, G and I. IgM (A) and C3d (B) deposition are observed in astrocytic vascular foot processes as well as in degenerated astrocytes (arrowheads). (C, D) Serial sections from a more advanced active lesion in the spinal cord from NMO‐7. IgG (C) and IgM (D) deposition are observed in astrocytic vascular foot processes as well as degenerated astrocytes (arrowheads). (E–H) Serial sections of an active lesion from NMO‐10 without immunoglobulin/complement deposition. These figures show the periplaque, still‐myelinated areas of the lesion shown in Figure 1A–F. Although GFAP immunoreactivity is preserved (E), AQP4 expression is totally lost (F). Neither C9neo (G) nor IgG (H) staining shows specific perivascular deposition. (I, J) Lack of immunoglobulin/complement deposition in MS. Serial sections of a chronic active lesion from MS‐4. These figures show the same area as in Figure 4K and L. Neither IgG (I) nor C3d (J) staining shows typical perivascular deposition. (K–M) Lymphocyte cuffing in MS and NMO. (K, L) Serial sections from an active lesion from MS‐3. These figures show the same lesion as in Figure 4E and F. K. CD45RO staining demonstrates perivascular cuffing predominantly consisting of T cells. L. Few CD20‐positive B cells in the perivascular area. M. An active lesion in the spinal cord from NMO‐7. This figure shows the same lesion as in C and D. Although CD45RO‐positive T‐cells predominate, the degree of perivascular lymphocyitic accumulation is much milder in NMO than in MS. A, D, IgM immunohistochemistry (IHC); B, J, C3d IHC; C, H, I, IgG IHC; G, C9neo IHC; E, GFAP IHC; F, AQP4 IHC; K, M, CD45RO IHC, L, CD20 IHC. Scale bar = 100 µm (K, L); 50 µm (A–J, M). AQP4 = aquaporin‐4; GFAP = glial fibrillary acidic protein; KB = Klüver‐Barrera staining; MS = multiple sclerosis; NMO = neuromyelitis optica.
