Figure 1.
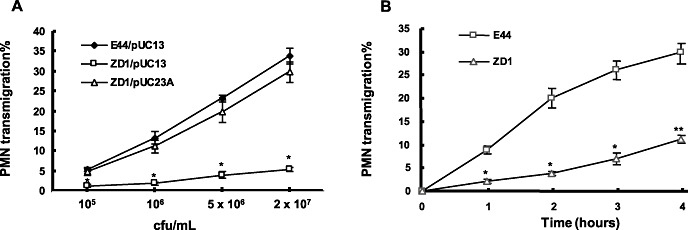
Dose‐dependent induction of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) transmigration across brain microvascular endothelial cell (BMEC) monolayers by E. coli strains E44, ZD1 and the complemented ZD1. PMN transmigration assays were performed as described in the Materials and Methods section. A. Induction of PMN migration with different doses (1 × 105 to 2 × 107 cfu/mL) [corresponding to 2.5–500 multiplicity of infection (MOI)] of E. coli K1 strains. Bacteria E44/pUC13 (IbeA+), ZD1/pUC13 (IbeA‐) and the complemented ZD1 (ZD1/pUC23A)(IbeA+) were used in PMN migration assays. B. Time‐course study of E44‐ and ZD1‐induced PMN transmigration across human BMEC monolayers. PMN transmigration was triggered by 5 × 106 cfu/mL (corresponding to 125 MOI) of E. coli strain E44 or ZD1. PMN migration in response to ZD1 was significantly reduced at all time points between 1 and 4 h after addition of PMN to the human BMEC monolayer. The values represent the mean percent transmigrating PMN of triplicate samples and are representative of one experiment from three independent experiments showing similar data. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with E44.
