Figure 8.
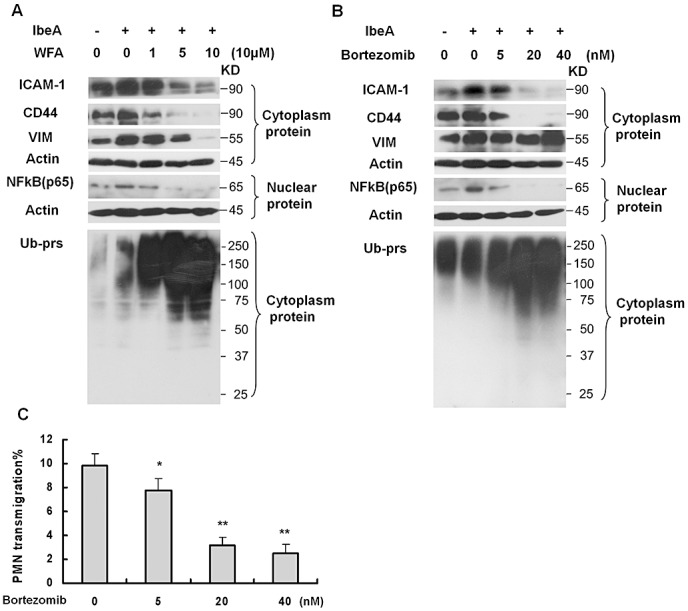
Regulation of adhesion molecule (ICAM‐1 and CD44) expression that is associated with IbeA‐induced polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) transmigration. (A,B) Immunoblotting analysis of adhesion molecules (ICAM‐1 and CD44), VIM, nuclear NFκB (p65) and polyubiquitinylated proteins. Human brain microvascular endothelial cell (HBMEC) treated with WFA (1–10 µM) (A) or brothemib (5–40 nM) (B) for 0.5 h and then incubated with the IbeA protein (0.5 µg/mL) for 6 h. In both (A) and (B), the cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were extracted as described in the Methods section. To determine the proteasome activity, cytoplasmic polyubiquitinylated proteins (Ub‐prs) were immunoblotted with polyubiquitinylated proteins mAb. Cytoplasmic‐actin and nuclear β‐actin were used as internal loading controls, respectively. In all experiments, untreated HBMEC were used as controls. C. Inhibition of PMN transmigration across HBMEC after pre‐incubation with different doses of brothemib at the indicated concentration (5–40 nM) at 37°C for 1 h. PMN transmigration was triggered by E44 (25 MOIs). The values represent the mean % transmigrating PMN of triplicate samples. The significant differences between treated and untreated cells were marked by asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).
