Figure 4.
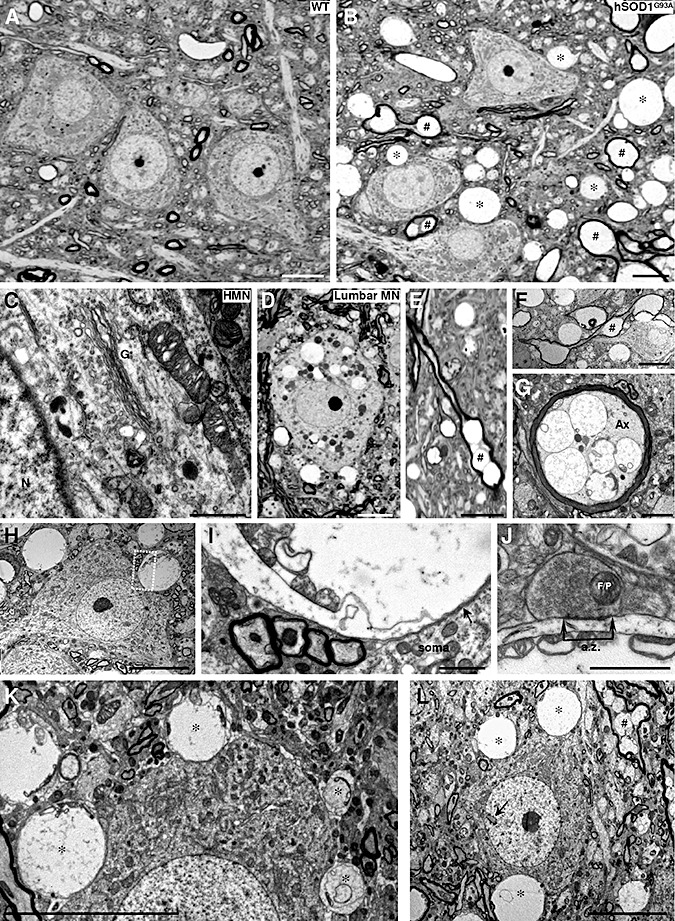
Neuropathological alterations in the hypoglossal nucleus (HN) of 3‐month‐old hSOD1G93A mice. A. B. Photomicrographs of semi‐thin sections from the HN of a 3‐month‐old wild‐type (WT) non‐transgenic (A) mouse compared to an age‐matched hSOD1G93A transgenic mouse (B). Vacuolated and swollen myelin‐wrapped axons (#) and feasible dendrites (*) are evidenced in the transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. C. Details of the soma of a hypoglossal motoneuron (HMN) taken with electron microscopy, showing microvacuoles into mitochondrion and cytoplasm, as well as disorganization of the Golgi apparatus (G). N, nucleus. D. Vacuolated perikarya of a lumbar motoneuron (lumbar MN) in the same mouse as in C. E–G. Photomicrographs from semi‐ (E) and ultra‐thin (F, G) sections showing longitudinally (E, F; #) and transversally (G) transected myelin‐wrapped axons. Note the vacuoles containing remnants of mitochondria observed in the axon (Ax) shown in G. H, I. A HMN from a SOD1G93A mouse at 90 days postnatal with a vacuolated structure apposed to its plasma membrane. The boxed area in H is presented at higher magnification in I. Note that the membrane of the vacuolated structure containing mitochondria vestiges is apposed to the plasma membrane of the motoneuron (arrow). J. Detail of a bouton containing flat/pleomorphic (F/P) vesicles showing an active zone (a.z.) apposed to a post‐synaptic density on a vacuolated structure with mitochondria remnants. This supports the dendritic nature of the degenerating structure. K. In this photomicrography four different‐sized vacuolated structures (*), containing mitochondria residues, appear close to the soma membrane of a HMN. This could represent the pathological progression for the formation of a large vacuolated structure. Note that the larger the vacuole, the greater the deformation that is induced in the apposed motoneuron. L. Example of a hypoglossal interneuron identified by its invaginated nucleus (arrow) surrounded by vacuolar structures. Scale bars: A, B, D–F, H, K, L, 10 µm; G, I, 2 µm; C, J, 1 µm.
